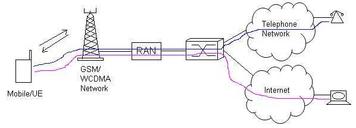
Circuit Switched vs. Packet Switched Calls: Key Differences
Explore the differences between circuit-switched and packet-switched calls. Understand how they work, their best applications, and call flow examples for GSM and WCDMA networks.
Showing 16 posts (Page 1 of 1)
Advertisement

Explore the differences between circuit-switched and packet-switched calls. Understand how they work, their best applications, and call flow examples for GSM and WCDMA networks.
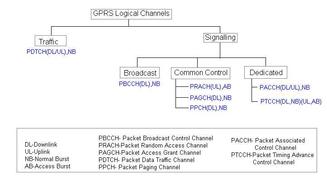
Explore GPRS, a packet-switched technology for data connections over GSM networks. Learn about its architecture, frame structure, channels, and more.

What is cs and ps in telecom - Understand key differences between Circuit switching and packet switching with examples used for voice and data communication.
Explore the distinctions between Frame Relay and X.25, two packet-switching technologies, focusing on their error handling, layers, and bandwidth allocation.

Explore the pros and cons of Frame Relay technology, a packet-switching protocol for high-speed data communication in WANs. Learn its benefits and drawbacks.
Explore the key features and advantages of GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) in mobile data communication. Learn how it enhances GSM networks.

Learn about the packet switched (PS) call flow in GSM downlink for data transfer. Understand GPRS attach, PDP context activation, and the channels involved.

Explore the packet switched (PS) data call flow in GSM uplink, detailing GPRS attach and PDP context activation between mobile devices and network elements.
Explore the fundamental differences between GSM and GPRS technologies, focusing on their architecture, timeslot allocation, traffic types, and network elements.

This article compares MPLS label switching and IP packet switching, highlighting their differences in routing, path establishment, and forwarding tables.

Explore fundamental networking concepts, including switching, addressing, OSI/TCP/IP layers, and network devices like hubs, switches, and routers.

A comparison of optical circuit switching (OCS), optical burst switching (OBS), and optical packet switching (OPS), covering their functionalities, advantages, and disadvantages.

Explore the differences between packet switching and message switching, comparing overhead, reliability, time efficiency, and complexity.

Explore 5 benefits and drawbacks of packet switching, a technology used for data and voice transmission. Learn about its efficiency, reliability, and limitations.

Explore the X.25 protocol, covering its benefits such as reliability and faster response times, as well as its drawbacks, including low data rates and overhead.

Explore the X.25 protocol stack, including the physical (X.21), frame (LAPB), and packet (PLP) layers. Learn about frame structure and how these layers ensure robust network communication.
Advertisement