GPRS: Key Features and Benefits in Data Communication
Advertisement
Introduction
GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) revolutionized data communication by enabling efficient and cost-effective mobile internet access. It acts as an enhancement to GSM networks, providing users with packet-switched data services for browsing, emailing, and multimedia sharing. This guide delves into the key features and benefits of GPRS, showcasing its impact on mobile data connectivity.
What is GPRS?
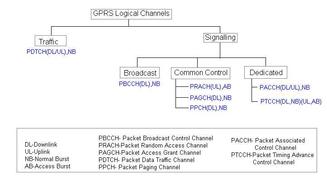
GPRS stands for General Packet Radio Service. GSM was initially designed for circuit-switched networks. GPRS added packet-switching functionality to the GSM network. GPRS was added to GSM specifications in release 97. This enabled the delivery of internet on mobile devices connected to the GSM network.
It’s important to check whether the GPRS feature is available on a mobile device before purchasing it if you intend to use it. GPRS delivers data rates of about 50 Kbps, compared to its predecessor GSM, which had about 9.6 kbps.
Key Features of GPRS
- Packet-Switched Data: Allows data to be sent and received in packets, optimizing network usage. Instead of a dedicated connection, data is broken down and sent in small packets, sharing resources more efficiently.
- Always-On Connectivity: Provides an always-connected experience without requiring reconnections. You’re always “online” and ready to send or receive data.
- Higher Data Rates: Offers speeds of up to 171.2 kbps, enabling basic internet usage. While slow by today’s standards, it was a significant improvement over GSM.
- Seamless Integration: Works as an enhancement to existing GSM networks. This made it easier for carriers to upgrade their networks and offer data services.
- Multimedia Support: Enables MMS, internet browsing, and email services. This opened up new possibilities for mobile communication.
- Dynamic IP Allocation: Supports IP-based services with efficient address allocation. Devices are assigned IP addresses as needed, optimizing address usage.
Advantages of GPRS
Following are some of the benefits of GPRS technology:
- Enhanced Mobile Internet: Makes mobile web browsing possible and convenient. Even with slower speeds, GPRS made accessing web content on the go a reality.
- Cost Efficiency: Charges are based on data usage rather than connection time. You only pay for the data you use, making it more economical than circuit-switched connections.
- Scalable for IoT: Supports basic IoT applications with its low data rates. GPRS can be used for simple data collection and control in IoT devices.
- Global Availability: Compatible with GSM networks worldwide. This widespread compatibility made GPRS a valuable technology for international roaming.
Conclusion
GPRS remains a pivotal technology in mobile data communication, bridging the gap between traditional GSM and advanced 3G/4G networks. Its features have paved the way for a more connected and data-driven mobile experience.
Advertisement
 RF
RF