GSM Uplink Packet Switched Data Call Flow
Advertisement
This tutorial covers the Packet Switched (PS) data call flow between a Mobile device (UE) and the network for uplink (data upload). It details the messages exchanged during GPRS attach and PDP context activation procedures between the mobile device and SGSN/VLR/HLR/GGSN.
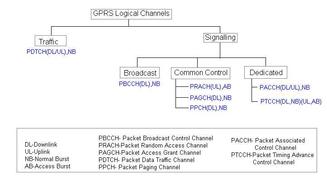
It also highlights the channels (PPCH, PRACH, AGCH, PDCH) used at Layer 1 to carry these messages over the air.
This article assumes that the initial frequency and time synchronization has been completed between the UE and the Network, as described in the GSM tutorial.

Here, RACH (Random Access Channel) is sent by the mobile (UE) to the network (BTS), and the network will assign a slot (single/multiple) for packet transfer.
GPRS attach procedures are completed by the mobile station for location updates and to complete security checks.
To establish internet connectivity, an IP address needs to be assigned to the Mobile, and connectivity with the APN (Access Point Name) needs to be established. This is done using PDP (Packet Data Protocol) context activation procedures.
As described in the GSM protocol stack, messages flow between both the mobile device and the network at various layers (Layer 3, Layer 2, Layer 1 (physical layer)).
The message flow is self-explanatory in establishing the Packet Switched uplink data call in GSM.
Advertisement
 RF
RF