Wi-Fi 7 Channel List: Frequency Channels Explained
Explore Wi-Fi 7 channel allocations, frequencies, and bandwidths. Understand how Wi-Fi 7 optimizes spectrum use and enhances data rates with features like Multi-Link Operation.
Advertisement
Explore Wi-Fi 7 channel allocations, frequencies, and bandwidths. Understand how Wi-Fi 7 optimizes spectrum use and enhances data rates with features like Multi-Link Operation.
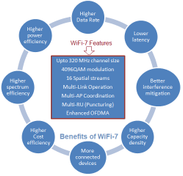
Explore the pros and cons of Wi-Fi 7 (IEEE 802.11be), including its high speeds, reduced latency, increased complexity, and power consumption.

Learn about Wi-Fi Direct technology, which enables direct Wi-Fi connections between devices without an access point. Explore its benefits and applications.

Explore the differences between WiFi 4 (802.11n) and WiFi 5 (802.11ac), including speed, range, bandwidth, and other parameters.

Explore the pros and cons of WiFi 6 (802.11ax), including increased data rates, improved efficiency, and potential drawbacks.
Explore the differences between WiFi 6, WiFi 6E, and WiFi 7, including speed, features, and use cases, to understand which wireless technology best suits your needs.

Explore the key differences between WiFi 6 and WiFi 7, including data rates, frequency bands, modulation, MIMO, and channel size.

Explore the key differences between WiFi 6E and WiFi 7, focusing on their performance, bandwidth, and suitability for various applications.

Explore the differences between WiFi 6E and WiFi 6, focusing on spectrum, speed, latency, and applications. Discover how WiFi 6E enhances WiFi 6 with the 6 GHz band.

Explore the pros and cons of WiFi 6E, an extension of WiFi 6 using the 6 GHz band, offering faster speeds, lower latency, and improved performance.

Explore WiFi 7 Multi-Link Operation (MLO) for increased data rates, lower latency, and improved reliability. Learn about MLO modes, architecture, and benefits as per the IEEE 802.11be standard.
Explore the similarities and differences between WiFi 7 (802.11be) and WiFi 8 (802.11bn), focusing on data rates, features, and target applications.

Explore WiFi 7 (IEEE 802.11be), its key features like 320 MHz channels, 4096 QAM, MU-MIMO, and Multi-Link Operation, and the benefits it offers over previous WiFi generations.
Explore WiFi 7's DCM and DCM-DUP, designed to improve signal robustness and coverage by duplicating data across subcarriers or channels for enhanced reliability.

An overview of WiFi 8 (IEEE 802.11bn), the next generation of wireless networking, focusing on planned features like mmWave, multi-link operation, and increased reliability.

Explore the key differences between WiFi boosters and WiFi repeaters, including signal amplification and channel frequency conversion.

Explore the differences between WiFi bridges and access points, and how they extend wireless network coverage. Learn about their functions and key features.
Explore the distinctions between WiFi extenders and routers in terms of coverage, internet connectivity, standalone operation, ports, and cost. Understand how they work together to enhance WiFi.

Explore the evolution of WiFi technology, from the original 802.11b to the latest WiFi 6 (802.11ax). Compare speeds, range, and key features across all generations.
Explore WiFi HaLow (WiVi) technology, designed to extend WiFi coverage with low power consumption. Learn about its features, specifications, and applications in IoT networks, adhering to the IEEE 802.11ah standard.
Advertisement