WiFi 6 vs WiFi 7: Key Differences Explained
Advertisement
This article compares WiFi 6 and WiFi 7, highlighting their similarities and differences.
Introduction:
The IEEE develops Wi-Fi standards within the 802.11 series (e.g., 802.11b, g, n, ac, ax, and be). The WiFi Alliance certifies products built according to these standards. WiFi 7 represents the future of Wi-Fi, designed to support demanding real-time applications like video streaming, wireless gaming, telemedicine, edge/cloud computing, AR/VR, industrial IoT, and video conferencing.
What is WiFi 6?
WiFi 6 adheres to the IEEE 802.11ax specifications, introduced in 2019. The standard has been finalized, and Wi-Fi 6 devices are now commercially available. WiFi 6 offers approximately 40% faster data rates compared to its predecessor, WiFi 5. It operates on both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands. WiFi 6E extends Wi-Fi’s capabilities into the 6 GHz band, where “E” signifies “Extended.”
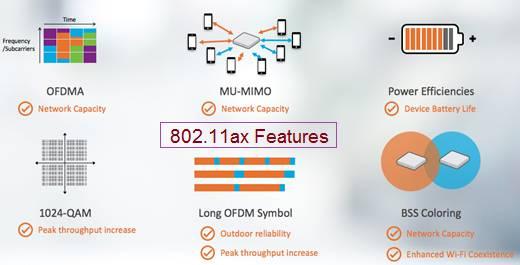
Image Courtesy: Ruckus Networks
Key features of WiFi 6:
- Higher modulation scheme: Up to 1024-QAM
- Longer OFDM symbol duration
- MU-MIMO in both uplink (UL) and downlink (DL), supporting 8 simultaneous MU-MIMO streams
- Beamforming and OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access) techniques
- Uplink scheduling without contention
- BSS (Basic Service Set) color codes
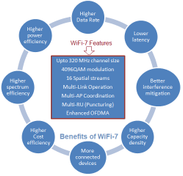
What is WiFi 7?
IEEE is currently developing WiFi 7 specifications under the 802.11be series. It will support double the bandwidth and a greater number of spatial streams compared to WiFi 6 (802.11ax). WiFi 7 aims to achieve data rates as high as 40 Gbps and is projected to launch in 2024. The IEEE 802.11be EHT (Extremely High Throughput) working group is responsible for its development.
Key features of WiFi 7 include:
- Coordinated Multi-user MIMO (CMU-MIMO) to simultaneously support 16 data streams.
- Multi-Link Operation (MLO): Enables simultaneous transmission and reception across different bands/channels, improving throughput, reducing latency, and enhancing reliability.
- Access Point coordination
- Maximum channel size support of up to 320 MHz
- Higher modulation schemes: Up to 4096 QAM with enhanced OFDMA
WiFi 6 vs WiFi 7: A Detailed Comparison
The following table compares WiFi 6 and WiFi 7 based on various parameters:
| Features | WiFi 6 and WiFi 6E | WiFi 7 |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | IEEE 802.11ax | IEEE 802.11be |
| Launch date | 2019 (WiFi 6), 2021 (WiFi 6E) | 2024 |
| Data rate (Maximum) | 9.6 Gbps | 46 Gbps |
| Frequency Bands | 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, 6 GHz (WiFi 6E) | 1 to 7.25 GHz (2.4, 5, and 6 GHz) |
| Security | WPA 3 | WPA 3 |
| Channel Size | 20, 40, 80, 80+80, 160 MHz | Up to 320 MHz |
| Modulation | 1024 QAM with OFDMA | 4096 QAM with OFDMA (extensions) |
| MIMO | MU-MIMO (8 data streams simultaneously) | CMU-MIMO (16 data streams) |
| Resource Allocation | Single RU | Multi-RU |
References: IEEE, WiFi Alliance, Intel Corporation.
Conclusion
Wi-Fi 7 builds upon the foundation of Wi-Fi 6 by significantly enhancing speed, efficiency, and network capacity. While Wi-Fi 6 operates on 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz bands with a maximum speed of 9.6 Gbps, Wi-Fi 7 leverages the same bands but introduces 320 MHz channel bandwidth, 4K-QAM modulation, and Multi-Link Operation (MLO), enabling speeds up to 46 Gbps. These advancements make Wi-Fi 7 ideal for ultra-low latency applications like AR/VR, cloud gaming, and 8K video streaming. With improved interference management and enhanced multi-device connectivity, Wi-Fi 7 is set to redefine wireless networking for high-performance, future-ready applications.
Advertisement
 RF
RF