Understanding GPRS: A Terminology Guide
Advertisement
This page describes terms related to the GPRS standard, covering what GPRS is, the GPRS frame structure, SGSN, GGSN, TBF, TFI, EDGE, BEP, EDA, CS1 to CS4 GPRS coding schemes, GPRS interfaces, MMS, etc.
| GPRS Terms | Basic Description | RF Wireless World Reference |
|---|---|---|
| What is GPRS | General Packet Radio Service, the packet-centric data communication standard for cellular technologies such as GSM and WCDMA. Mainly used in GSM. | |
| GPRS frame structure | The frame structure used between a Base Station and GPRS compliant UE for communication and exchange of data as well as control information. | |
| SGSN | Serving GPRS Support Node | |
| GGSN | Gateway GPRS Support Node | |
| TBF | Temporary Block Flow | |
| TFI | Temporary Flow Identity | |
| EDGE | Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution | |
| BEP | Bit Error Probability | |
| EDA | Extended Dynamic Allocation, the scheme by which a subscriber (UE) can use a number of time slots in the uplink, unlike DA (Dynamic Allocation) method. Here, the UE needs to decode USF just once and can transmit the data over the time slots until the next block period. | |
| CS1, CS2, CS3, CS4 | Coding schemes used in GPRS to facilitate different data rates for the UE. Different schemes support different data rates. | |
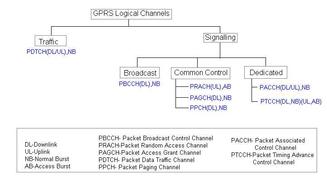
| GPRS Interfaces | The interfaces are the signal connections by which different GPRS network elements are interconnected. | |
| MMS | Multimedia Message Service, the service by which bigger messages can be transmitted over a GPRS network. |
Advertisement
 RF
RF