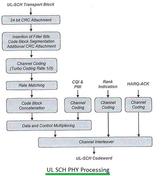
LTE UL-SCH Physical Layer Processing
Explores the LTE UL-SCH function and the physical layer processing steps for the transmitter, culminating in the generation of the SC-FDMA signal.
Showing 20 posts (Page 8 of 11)
Advertisement

Explores the LTE UL-SCH function and the physical layer processing steps for the transmitter, culminating in the generation of the SC-FDMA signal.

Explore the key differences in physical layer timing between LTE and 5G NR, including formulas for sampling time, frame duration, and subframe duration.
Explore the key differences between LTE, 5G TF (Technical Forum), and 5G NR (New Radio) technologies, covering specifications and physical layer aspects.
Explore the distinctions between LTE and LTE Advanced, two 4G technologies. Learn about data rates, bandwidth, carrier aggregation, and more in this comparative overview.
Explore the key differences between LTE and LTE-M technologies, focusing on their use cases, power consumption, cost, coverage, and data rates for IoT applications.
Explore the differences between LTE and NB-LTE (NB-IoT) technologies, comparing specifications like bandwidth, latency, battery life, and more.
Explore the key differences between LTE (Long Term Evolution) and UMB (Ultra Mobile Broadband) technologies, including multiple access schemes, channel coding, and duplexing methods.

Explore the differences between LTE and VoLTE technologies, focusing on voice call handling, call quality, setup times, and battery efficiency within all-IP networks.
Explore the key differences between LTE and WLAN, including their technologies, applications, coverage, and performance characteristics.

Understand the LTE-M frame structure, including hyperframes, frames, subframes, slots, and the PRB pair. Explore its constituents and how it relates to LTE.
Overview of LTE-M frequency bands, focusing on bands 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 12, 13, 20, and 28, including deployment countries and operators.

Explore the LTE-M protocol stack, including the user and control planes, and the functions of each layer: PHY, MAC, RLC, PDCP, and RRC.

Learn about LTE-M (LTE Cat-M1), a Low Power Wide Area (LPWA) technology for IoT, covering architecture, frequency bands, and protocol stack.
Explore the key differences between LTE-M and NB-IoT technologies, including specifications, bandwidth, coverage, and data rates, for LPWAN applications.
Explore the MIB (Master Information Block) and SIBs (System Information Blocks) in LTE-NB and NB-IoT, covering their functions and contents.
Explore the differences between LTE-U, LAA, LWA, and Multefire technologies, focusing on their advantages, disadvantages, and use cases within LTE and 5G networks.

Learn about LTE (Long-Term Evolution), the 4G mobile communication standard. Discover its features, benefits, and how it transformed mobile connectivity.
A comprehensive list of companies that develop and offer MAC (Medium Access Control) IP cores for various wireless technologies like WLAN, WiMAX, LTE, and Zigbee.
MediaTek's new multimode modem supports LTE Release 9 and is backward compatible with GSM, GPRS, EDGE, DC-HSPA+, WCDMA, and TD-SCDMA technologies.

Explore the roles of MME, PGW, and SGW in LTE networks, highlighting their functions, differences, and significance in managing user mobility and data routing.
Advertisement