GSM BTS Transceiver Power Class Explained
Understand the GSM BTS Transceiver Power Class, covering maximum output power for different GSM bands including GSM-400, GSM-900, DCS-1800, and PCS-1900.
Showing 20 posts (Page 2 of 6)
Advertisement
Understand the GSM BTS Transceiver Power Class, covering maximum output power for different GSM bands including GSM-400, GSM-900, DCS-1800, and PCS-1900.
Understand GSM timing advance errors, their impact on burst measurements, and how test systems like the Rohde & Schwarz CRTU validate mobile transmissions.
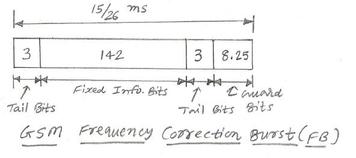
Learn about the different types of GSM bursts (Normal, Frequency Correction, Synchronization, Access) and their roles in ensuring proper communication between mobile and base stations.

Calculate GSM C1 and C2 parameters for cell selection and reselection. Includes formulas and an example calculation.

Explanation of GSM combined channel configuration for Time Slot 0 (TS0) in the 51-frame multiframe, mapping FCCH, SCH, BCCH, CCCH, SDCCH, and SACCH channels.
GSM Common Control Channels (CCCHs) facilitate communication between the network and mobile subscribers, conveying information and providing network access.

Explore GSM control channel processing in the physical layer, covering SACCH, FACCH, BCCH, PCH, AGCH, and more, as per 3GPP TS 45.003.

Learn about the packet switched (PS) call flow in GSM downlink for data transfer. Understand GPRS attach, PDP context activation, and the channels involved.

Learn about the GSM Fast Associated Control Channel (FACCH), used for rapid information exchange between a mobile station and base transceiver station.
Overview of Frame Error Rate (FER) testing limits for GSM user equipment (UE) in the 900MHz and 1800MHz frequency bands according to 3GPP TS 51.010.

The GSM Frequency Correction Channel (FCCH) is a downlink channel used for synchronization between the BTS and MS by transmitting a continuous wave signal.
This article explains GSM handover failures from UTRAN due to physical channel issues, leading to timer T313 expiry, and outlines the handover procedure.

Explore the causes and triggers of GSM handover, a crucial process for maintaining uninterrupted mobile connections. Learn about signal strength, quality, distance, speed, traffic load, and maintenance triggers.
Explore the causes of GSM handover and cell reselection failures due to CRC errors, including interference, power issues, and algorithm limitations.

Calculate the IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity) using the GSM IMEI formula. Understand the components and generate valid IMEI numbers.
Explanation of a GSM network issue where a UE sends a SABM frame but receives a DM response instead of the expected UA, indicating connection establishment failure.

Learn about GSM Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and the Call Setup Success Rate (CSSR) formula. Use our online calculator to determine CSSR values in GSM networks.
Understand GSM logical channels (TCH, BCCH, CCCH, DCCH) used in 2G networks for transmitting user data, control, and signaling information between mobile devices and the network.
Explore GSM mobile station measurements, including RSSI, frequency error, and receiver sensitivity, crucial for network optimization and conformance testing.

Explore the GSM Mobile Originated (MO) call flow, detailing the messages exchanged between the mobile device and network layers during call setup and release.
Advertisement