
GSM Control Channel Processing Through Physical Layer
Explore GSM control channel processing in the physical layer, covering SACCH, FACCH, BCCH, PCH, AGCH, and more, as per 3GPP TS 45.003.
Showing 20 posts (Page 7 of 20)
Advertisement

Explore GSM control channel processing in the physical layer, covering SACCH, FACCH, BCCH, PCH, AGCH, and more, as per 3GPP TS 45.003.

Learn about the packet switched (PS) call flow in GSM downlink for data transfer. Understand GPRS attach, PDP context activation, and the channels involved.
Overview of Frame Error Rate (FER) testing limits for GSM user equipment (UE) in the 900MHz and 1800MHz frequency bands according to 3GPP TS 51.010.
This article explains GSM handover failures from UTRAN due to physical channel issues, leading to timer T313 expiry, and outlines the handover procedure.
Explore the causes of GSM handover and cell reselection failures due to CRC errors, including interference, power issues, and algorithm limitations.
Explanation of a GSM network issue where a UE sends a SABM frame but receives a DM response instead of the expected UA, indicating connection establishment failure.

Explore the GSM Mobile Originated (MO) call flow, detailing the messages exchanged between the mobile device and network layers during call setup and release.

Understand the GSM Mobile Terminated (MT) call flow, including message exchanges between the UE and network layers, and channels used.
Explore GSM packet-switched channels, focusing on GPRS (CS1-CS4) and EGPRS (MCS1-MCS9) coding schemes at the physical layer. Understand data rates and robustness trade-offs.

Explore the GSM physical layer (layer-1) functions, including baseband processing, FEC, ciphering, burst formation, and modulation for mobile station transmission.

Explore the GSM protocol stack and architecture for Mobile Stations (MS) and Base Transceiver Stations (BTS), covering Layer 1 (PHY) and Layer 2 (LAPD, LAPDm).

Explore GSM Layer 3 responsibilities, covering RRM, MM, CM, SCCP, and BSSMAP protocols. Understand message types and protocol discriminators.
Explores the causes and mechanisms behind radio link failure in GSM networks, covering both mobile and network perspectives.

Explore GSM traffic channel processing through the physical layer, covering speech and data channels as per 3GPP TS 45.003.

Explore the packet switched (PS) data call flow in GSM uplink, detailing GPRS attach and PDP context activation between mobile devices and network elements.

Explore the key differences between GSM and CDMA cellular technologies, including their technical specifications, network structures, and historical significance in mobile communication.
This article explains the PLMN not found issue in GSM networks, focusing on causes like weak signals, interference, network failures, and roaming data.
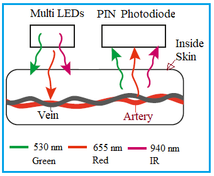
Explore health monitoring systems using LEDs and photodiodes for heart rate and SpO2 measurement, covering system architecture, key components, and principles.
Explore the fundamentals of heat detectors, comparing fixed temperature and rate of rise types, and their operational differences.
Convert between hex and decimal numbers in fixed-point format using C code. Includes handling positive/negative values and explanation of Q format.
Advertisement