Transmit Power Accuracy & RSSI Measurement in WiFi 7 (IEEE 802.11be)
Advertisement
In Wi-Fi 7 (IEEE 802.11be), transmit power accuracy and Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) measurement are critical parameters that ensure reliable and consistent wireless communication. They are important for optimizing performance, managing interference, and facilitating network planning and troubleshooting.
Transmit Power Accuracy
Transmit power accuracy refers to how closely the actual transmit power of a Wi-Fi 7 device matches the intended or configured power level. Accurate control of transmit power is essential for maintaining consistent network performance, minimizing interference with other devices, and complying with regulatory limits.
Key Points of Transmit Power Accuracy
- Definition: Transmit power accuracy specifies the allowable deviation between the intended transmit power and the actual power output from the transmitter. This is typically expressed in decibels (dB).
- Precise control of transmit power helps to reduce interference with other nearby Wi-Fi devices and networks.
- Adhering to power limits specified by regional regulations ensures devices do not exceed maximum permissible exposure levels, which is crucial for legal operation.
- Accurate power levels ensure optimal link quality and network coverage, which can be critical in densely populated wireless environments.
Requirements
Wi-Fi 7 specifies tight accuracy requirements to ensure consistent performance. Typically, the transmit power accuracy must be within +/- 2 dB of the intended level. This means if a device is set to transmit at 20 dBm, the actual output should be between 18 dBm and 22 dBm.
Following are the factors which affect accuracy:
- Temperature Variations: Temperature changes can affect the performance of power amplifiers and other RF components, impacting transmit power levels.
- Aging and Component Tolerances: Over time, component degradation and manufacturing variances can lead to deviations in power output.
Testing and Calibration
- Calibration: Devices are typically calibrated during manufacturing to meet the transmit power accuracy requirements. Ongoing adjustments may be made in real-time to compensate for environmental or hardware variations.
- Testing: Compliance is tested by measuring the output power at various transmit levels and verifying that it falls within the specified accuracy range.
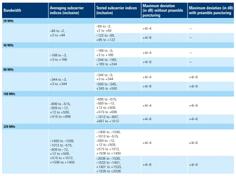
| Parameter | Class A devices (11be minimum requirements) | Class B devices (11be minimum requirements) | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute transmit power accuracy | +/- 3 dB | +/- 9 dB | Accuracy of achieving a specified transmit power level |
| Relative transmit power accuracy | Not applicable | +/- 3 dB | Accuracy of the change in transmit power for consecutive EHT TB PPDU |
| RSSI measurement accuracy | +/- 3 dB | +/- 5 dB | Difference between the measured RSSI and the received power |
The table mentions absolute/relative transmit power accuracy and RSSI measurement accuracy minimum requirements for class-A and class-B devices as per IEEE 802.11be standard specifications.
RSSI Measurement in Wi-Fi 7 (IEEE 802.11be)
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) measurement is used to estimate the power level of the received signal at the receiver. Accurate RSSI measurements are important for functions like rate adaptation, power control, and network diagnostics.
Key Points of RSSI Measurement
- Definition: RSSI is a measure of the signal strength of a received packet. It is expressed in dBm and provides an indication of the quality of the received signal.
- Purpose:
- Rate Adaptation: RSSI values are used by devices to adjust their modulation and coding schemes (MCS) dynamically. Higher RSSI usually allows for higher MCS and thus, higher data rates.
- Roaming Decisions: RSSI helps devices decide when to switch between access points to maintain the best connection quality.
- Power Control: Devices use RSSI feedback to adjust their transmit power for optimal performance and minimal interference.
Requirements
- Accuracy: Wi-Fi 7 specifies that RSSI measurements should be within +/- 5 dB of the actual received signal power. This ensures that the measurement is reliable enough for use in adaptive algorithms and network management functions.
- Consistency Across Devices: RSSI measurements must be consistent across different devices to ensure fair and efficient network operation.
Factors Influencing RSSI Accuracy
- Multipath and Fading: Physical phenomena like multipath and fading can cause fluctuations in the received signal strength, impacting RSSI readings.
- Interference: Nearby interference sources can affect RSSI accuracy by altering the perceived signal strength.
- Hardware Variations: Differences in antenna design, receiver sensitivity, and calibration can lead to variations in RSSI measurements.
Testing and Calibration
- Calibration: During device manufacturing, RSSI measurement accuracy is calibrated against known signal levels to ensure that devices can measure signal strength accurately.
- Measurement Process: RSSI is measured by the receiver as the average signal power over a packet’s duration, and the measurement is usually updated on a per-packet basis.
Summary
- Transmit Power Accuracy: Ensures that the device transmits at the correct power level within a specified tolerance (typically +/- 2 dB). This is crucial for maintaining reliable performance, minimizing interference, and complying with regulations.
- RSSI Measurement: Provides an estimate of the received signal strength, used for various adaptive functions like rate selection, power control, and roaming. RSSI measurements should be accurate within +/- 5 dB to ensure effective network operation.
- These parameters are vital for the robust performance of WiFi 7 networks, ensuring efficient use of spectrum, reliable connections, and optimal network management.
Advertisement
 RF
RF