Receiver Maximum Input Level in WiFi 7 (IEEE 802.11be)
Advertisement
In Wi-Fi 7 (IEEE 802.11be), the receiver maximum input level is a crucial parameter. It specifies the highest signal strength at which the receiver can operate correctly without significant performance degradation. This specification makes sure the receiver can handle strong signals without overloading, which is vital for reliable communication, particularly when a device is near a high-power transmitter.
The receiver maximum input level defines the upper limit of signal power the receiver can handle while still meeting required performance criteria, typically in terms of packet error rate (PER) or bit error rate (BER). Above this level, the receiver may saturate, leading to distortion, increased error rates, or even loss of connectivity.
Key Points of Receiver Maximum Input Level in Wi-Fi 7
Definition: The receiver maximum input level is the highest received power, measured in dBm, at which the receiver must operate correctly without excessive errors. This level ensures the receiver can manage strong signals typically encountered when devices are in close proximity to each other.
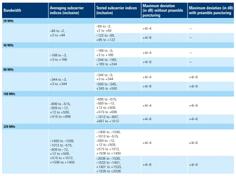
Typical Maximum Input Levels: For Wi-Fi 7, the maximum input level is generally defined as:
- For 20 MHz channels: Typically around -30 dBm.
- For wider bandwidths (40 MHz, 80 MHz, 160 MHz, 320 MHz): The maximum input level may be slightly less stringent due to the increased bandwidth collecting more noise and interference, but it usually remains around -30 dBm to -20 dBm depending on the exact modulation and coding scheme.
Performance Criteria: The receiver must maintain a specified performance level, such as a PER of 10% or lower, when receiving signals at the maximum input level. This performance criterion ensures that the receiver does not become overloaded and can still accurately decode signals at high input levels.
Impact of Exceeding Maximum Input Level:
- Nonlinearity and Saturation: If the input level exceeds the specified maximum, the receiver’s front-end amplifiers and analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) may become saturated, causing non-linear distortion and increasing error rates.
- Intermodulation and Crosstalk: Strong signals can cause intermodulation distortion, where signals mix and create spurious frequencies, or crosstalk between channels.
Testing and Compliance
Test Procedures: Receivers are tested by inputting signals at increasing power levels until the maximum specified level is reached. The receiver must continue to meet the performance criteria (e.g., a PER of 10% or better).
Equipment Used: Signal generators and test setups calibrated to precise power levels are used to evaluate receiver performance under these conditions.
Relevance in Real-world Scenarios
- High-density Environments: In environments like stadiums, airports, or dense urban areas where multiple devices are operating closely, strong signals can be prevalent. Ensuring that receivers can handle these levels without performance degradation is critical.
- Close Proximity to Access Points: Devices that operate close to access points or other transmitters need to handle high input power levels without errors, which is why maximum input level specifications are important.
Example of Maximum Input Level Requirements
- For a 20 MHz channel using 64-QAM with a 3/4 coding rate, Wi-Fi 7 may specify a maximum input level of -30 dBm. This means the receiver must handle signals up to -30 dBm without exceeding the defined PER threshold.
- For a 320 MHz channel using 4096-QAM, the maximum input level might still be around -30 dBm or slightly adjusted, ensuring that even with the highest modulation and wide bandwidth, the receiver can operate correctly under strong signal conditions.
- Packet error rate (PER) is measured at each physical antenna port and must be below 10 %. The measurement uses a PSDU length of 2048 octets for BPSK modulation with DCM or 4096 octets for all other modulations.
Importance of Maximum Input Level
- Ensures that the receiver can process strong signals without becoming saturated, which is essential for maintaining data integrity.
- By defining a maximum input level, Wi-Fi 7 devices can maintain reliable performance in various environments, from long-range connections to close-proximity scenarios.
- Consistent maximum input level specifications ensure that devices from different manufacturers can coexist and operate effectively in diverse deployment scenarios.
In summary, the receiver maximum input level in WiFi 7 (IEEE 802.11be) is designed to ensure that receivers can handle strong signals without performance degradation, supporting reliable communication in high-density and high-power scenarios.
Advertisement
 RF
RF