Ku Band Frequency: Values, Advantages, and Applications
Advertisement
This page explores Ku Band frequency, including its values, applications, and advantages.
| Frequency Band Designation | Frequency Range | Wavelength |
|---|---|---|
| Ku Band | 12 to 18 GHz | 2.5 to 1.7 cm |
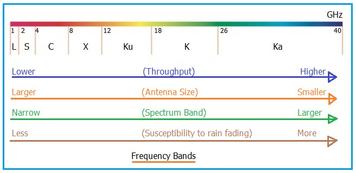
The Ku band frequency sits between the X Band and K Band in the electromagnetic spectrum, as illustrated in Figure 1 below.
As shown in the table, its frequencies span from 12 GHz to 18 GHz, corresponding to wavelengths between 1.7 centimeters and 2.5 centimeters.
Ku Band Frequency: Advantages and Disadvantages
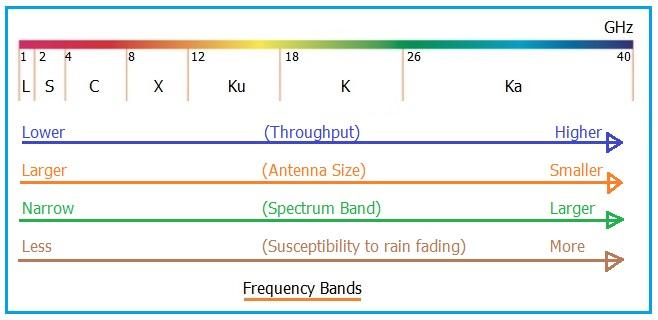
Here’s a look at the advantages of Ku Band frequency over other frequency bands:
- Smaller Antennas: It allows for the use of smaller dish antennas in VSAT applications. This leads to cheaper and easier installation.
- Higher Transponder Power: In certain scenarios, Ku band offers higher satellite transponder power.
- Reduced Terrestrial Interference: Ku band experiences less interference from terrestrial sources.
However, Ku band also has some disadvantages:
- Susceptibility to Rain Fade: Ku band signals are prone to rain fading, where heavy rain can significantly attenuate the signal.
- Narrow Beam Coverage: Due to its narrow beam, Ku band can cover a smaller area on Earth.
Ku Band Frequency Applications
Ku Band frequency has a variety of uses, including:
- Ku Band VSAT: Ku band VSAT systems utilize uplink frequencies from 14 to 14.5 GHz and downlink frequencies from 10.95 GHz to 11.7 GHz.
- Fixed Satellite Broadcast Services: It’s employed for fixed satellite broadcasting.
- NASA Space Shuttle Communication: Ku band is used for communication with space shuttles via NASA’s tracking data relay satellites.
- International Space Station Communication: NASA uses Ku band for communication with the International Space Station.
- VSAT Comparison: Refer to the difference between Ku Band and C Band for VSAT applications.
Advertisement
 RF
RF