Satellite Frequency Bands: Uplink and Downlink Ranges Explained
Advertisement
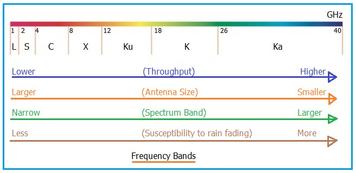
Satellite frequency bands are defined by their frequency range and are typically used for various applications like communication, broadcasting, and radar. Here is an overview of the primary satellite frequency bands along with their uplink and downlink ranges.
Satellite Frequency Band Overview
| Band | Frequency Range (GHz) | Uplink range (GHz) | Downlink range (GHz) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L band | 1-2 | 1.6 – 1.7 | 1.5 – 1.6 | GPS, mobile satellite services, maritime, and aviation communications. |
| S band | 2-4 | 2.5 – 2.7 | 2.1 – 2.3 | Satellite communications, telemetry, and weather radar. |
| C band | 4-8 | 5.9 – 6.4 | 3.7 – 4.2 | FSS (Fixed Satellite Service), television broadcasting, and telecommunications. |
| X band | 8-12.5 | 7.9 – 8.4 | 7.25 – 7.75 | Military communications, radar systems, and scientific research. |
| Ku band | 12.5-18 | 14.0 – 14.5 | 11.7 – 12.2 | Direct-to-home (DTH) television broadcasting, VSAT systems, and satellite Internet. |
| K band | 18-26.5 | 18.1 – 18.4, 21.2 – 22.0 | 17.7 – 21.2 | Used in radar systems, satellite communications, and for space research. It overlaps with parts of the Ka-band and Ku-band, and is less commonly used for commercial satellite services due to atmospheric attenuation at certain frequencies. |
| Ka band | 26.5-40 | 27.5 – 31.0 | 17.7 – 21.2 | High-capacity satellite communications, broadband Internet, and military satellite communications. |
| Q band | 33-42 | 33.0 – 36.0 | 36.0 – 42.0 | Experimental and high-frequency satellite communications. |
| V band | 37-50.2 | 47.2 – 50.2 | 37.0 – 42.5 | High-capacity satellite systems and future satellite communication systems. |
| U band | 48.2 - 51.4 | 50.4 – 51.4 | 48.2 – 50.2 | Primarily used in scientific and experimental contexts. |
These frequency bands are selected based on their propagation characteristics and specific application requirements, such as capacity, range, and penetration through atmospheric conditions.
Advertisement
 RF
RF