Ku vs. Ka Band: Differences in Satellite Communication
Advertisement
Satellite communication is vital for global connectivity, enabling services like TV broadcasting, internet access, and military communications. Among the various frequency bands used, Ku and Ka bands are particularly significant. Understanding the differences, advantages, and disadvantages of these bands is essential for selecting the right one for specific needs.
Ku Band Overview
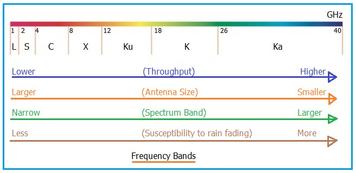
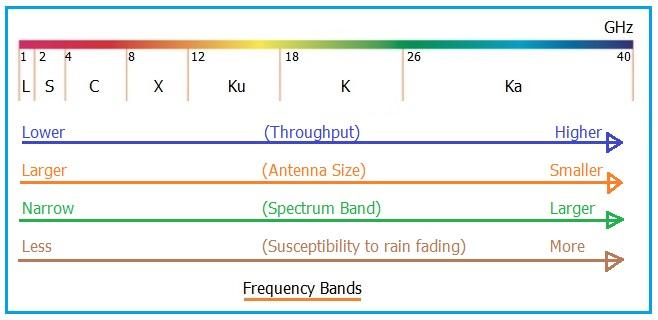
The Ku band operates in the frequency range of 12 to 18 GHz. This band offers a balance between capacity and performance. It’s primarily used for satellite communication, including TV broadcasting, VSATs (Very Small Aperture Terminals), and direct-to-home (DTH) services.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ku Band
Here’s a look at the pros and cons:
Advantages:
- Less Rain Attenuation: Ku band signals experience less attenuation due to rain compared to the Ka band, making them more reliable in adverse weather conditions.
- Widespread Deployment: It’s extensively deployed in TV broadcasting and VSAT systems, with widespread availability of equipment and infrastructure.
- Lower Equipment Costs: Equipment for the Ku band is generally less expensive compared to the Ka band due to the maturity of the technology.
Disadvantages:
- Congestion: The Ku band is quite crowded with many services, leading to potential interference and congestion issues.
- Lower Data Rates: Offers lower data rates compared to the Ka band, making it less suitable for high-speed internet applications.
Ka Band Overview
The Ka band operates in the frequency range of 26.5 to 40 GHz. It offers higher data rates and supports smaller dish sizes compared to lower frequency bands. It’s used for high-capacity satellite communications, including broadband internet services, satellite TV, and advanced military communication systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ka Band
Here’s a look at the pros and cons:
Advantages:
- Higher Data Rates: The higher frequency allows for increased bandwidth and higher data rates, suitable for broadband and high-capacity applications.
- Smaller Antennas: Due to the shorter wavelength, antennas and dishes can be smaller, which is beneficial for mobile and portable applications.
- Less Congestion: There is currently less congestion in Ka band frequencies, providing more available spectrum for new services.
Disadvantages:
- Rain Fade: Ka band signals are more affected by rain and atmospheric conditions, leading to potential service interruptions.
- Higher Costs: The equipment and deployment costs are generally higher due to the newer technology and the need for advanced weather mitigation techniques.
- Less Widespread Infrastructure: Ka band infrastructure is less widespread compared to the Ku band, which can limit accessibility in certain regions.
Difference between Ku and Ka Band
The following table compares Ku vs. Ka Band with respect to various parameters:
| Feature | Ku Band | Ka Band |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency range | 12 to 18 GHz | 26.5 to 40 GHz |
| Data rates | Lower | Higher |
| Antenna size | Larger | Smaller |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Rain Fade Susceptibility | Lower | Higher |
| Congestion | Higher (more crowded) | Lower (less crowded) |
| Availability | Widely available | Less widespread |
| Applications | Standard internet, TV services | High speed internet, advanced communication |
| Infrastructure | Mature and widely deployed | Emerging, less common |
| Primary uses | TV broadcasting, VSAT, DTH | Broadband internet, military, TV |
Summary
Ku and Ka bands are two of the most commonly used frequency bands in satellite communication, each with distinct characteristics. Choosing between these bands depends on factors like data rate requirements, cost considerations, and environmental conditions.
Advertisement
 RF
RF