
FDMA Vs TDMA: Key Differences Explained
Explore the differences between FDMA and TDMA, two multiple access techniques used in wireless communication, with examples and comparisons.
Showing 20 posts (Page 3 of 11)
Advertisement

Explore the differences between FDMA and TDMA, two multiple access techniques used in wireless communication, with examples and comparisons.

Explore the free duplex concept in 6G mobile, contrasting it with fixed and flexible duplex methods. Learn about its advantages, including increased throughput and improved spectrum efficiency.

Explore the fundamentals of Google Fi (formerly Project Fi), its network architecture, how it seamlessly switches between Wi-Fi and cellular, and device compatibility.
Understand GPRS multislot classes, including class 12, 32, and 33, with details on maximum slots supported in uplink and downlink.

Explore the GPRS protocol stack, detailing the functions of Layer 1, Layer 2, and Layer 3, including SM, GMM, SNDCP, LLC, RLC, MAC, and the physical layer.
Explore the relationship between RxQUAL (Receiver Quality) and BER (Bit Error Rate) in GPRS networks. Learn how RxQUAL relates to signal quality assessment.

Explore the pros and cons of GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) technology, including its compatibility, deployment, and data speeds.

Explore the key differences between GPS and U-TDOA technologies for device location, highlighting their methodologies, line-of-sight requirements, and effectiveness in emergency situations.

Learn about the GSM Access Grant Channel (AGCH), a downlink channel used to grant or deny network access and provide Traffic Channel (TCH) information.

Explore the GSM (2G) architecture, including Mobile Station, Base Station Subsystem, and Network Switching Subsystem, with detailed diagrams and explanations.
Convert GSM ARFCN values to corresponding uplink and downlink frequencies using our calculator. Understand the ARFCN to frequency relationship across GSM bands.

Learn about the GSM Broadcast Control Channel (BCCH), its role in system information broadcasting, and how mobiles use it to access the GSM network.
Understand the GSM BTS Transceiver Power Class, covering maximum output power for different GSM bands including GSM-400, GSM-900, DCS-1800, and PCS-1900.
Understand GSM timing advance errors, their impact on burst measurements, and how test systems like the Rohde & Schwarz CRTU validate mobile transmissions.
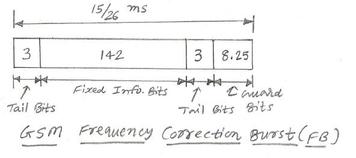
Learn about the different types of GSM bursts (Normal, Frequency Correction, Synchronization, Access) and their roles in ensuring proper communication between mobile and base stations.

Learn about the GSM Fast Associated Control Channel (FACCH), used for rapid information exchange between a mobile station and base transceiver station.
Overview of Frame Error Rate (FER) testing limits for GSM user equipment (UE) in the 900MHz and 1800MHz frequency bands according to 3GPP TS 51.010.

The GSM Frequency Correction Channel (FCCH) is a downlink channel used for synchronization between the BTS and MS by transmitting a continuous wave signal.

Explore the causes and triggers of GSM handover, a crucial process for maintaining uninterrupted mobile connections. Learn about signal strength, quality, distance, speed, traffic load, and maintenance triggers.
Understand GSM logical channels (TCH, BCCH, CCCH, DCCH) used in 2G networks for transmitting user data, control, and signaling information between mobile devices and the network.
Advertisement