
ADC Calculator: Analog to Digital Converter
Convert analog input to digital output using this ADC calculator. Explore the ADC conversion formula with examples for various bit resolutions.
Showing 14 posts (Page 1 of 1)
Advertisement

Convert analog input to digital output using this ADC calculator. Explore the ADC conversion formula with examples for various bit resolutions.

Explore the key differences between analog and digital signal processing, their applications, and the conversion processes involved.

Explore the fundamental differences between analog and digital signals, including their characteristics, advantages, and applications in various technologies.

Explore the benefits and drawbacks of bipolar line coding, including its implementation, bandwidth efficiency, and synchronization capabilities.
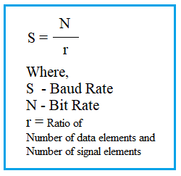
Explore the fundamental differences between data and signals in data communication. Learn how data is transformed into signals for transmission.

Explore the differences between encoding and modulation in data communication, with examples and advantages of each technique for signal conversion.

Explore the pros and cons of FSK modulation, covering its noise immunity and implementation simplicity, as well as bandwidth and power efficiency limitations.

Learn about HDMI to RF conversion, its necessity for connecting modern devices to older TVs, and considerations for choosing the right converter.

Explore the advantages and disadvantages of Non-Return-to-Zero (NRZ) pulse shapes in line coding, highlighting the benefits and drawbacks of NRZ encoding.

Explore the pros and cons of Pulse Code Modulation (PCM), including its robustness, bandwidth requirements, and quantization error.

Explore polar line coding techniques, including NRZ and RZ, with their benefits and drawbacks, such as DC voltage reduction and synchronization issues.

Explore RZ, NRZ, and Manchester codes used for digital signal transmission. Understand the key differences in pulse width and voltage transitions.

Explore the key differences between RZ and NRZ line coding, including unipolar, polar, and bipolar variations, with a focus on pulse shapes and their applications in digital communication.

Explore unipolar line coding, a basic digital encoding technique, including its principles, NRZ and RZ variations, benefits, and limitations like DC component and synchronization issues.
Advertisement