Analog vs. Digital Signal: Key Differences Explained
Advertisement
This page compares analog and digital signals, describing the key differences between them.
Introduction
Signals are categorized into two main types: analog and digital. These signals are used to transmit information from one end to another through a medium. Signals can also be periodic or aperiodic. Analog signals are continuous in nature, whereas digital signals are discrete.
Analog signals can be represented by a time-varying amplitude, such as a sine wave. Digital signals, however, can only be represented by one discrete value from a finite series of values, such as a binary signal. A binary signal uses either a one or a zero to represent the digital signal waveform, which looks similar to a series of square waves.
Analog Signal

Definition: A continuous waveform whose amplitude changes over time is known as an analog signal. The signaling technique that uses an analog signal is known as analog signaling.
An example of an analog signal is a sine wave, which cannot be decomposed any further. However, a composite analog signal can be decomposed into multiple sine waves. Analog signals are represented by three parameters: amplitude, frequency (or time period), and phase.
- Amplitude: Indicates the maximum height of the signal transition on the y-axis.
- Frequency: Indicates the rate of signal change with respect to time. Frequency is inversely proportional to the time period.
- Phase: Indicates the position of the sine wave with respect to zero time instant or some reference.
Analog signals are susceptible to interference from noise, which can lead to distortion and degrade the signal quality. This often requires filtering and amplification to achieve long-distance transmission and reception. The electromagnetic (EM) signal transmitted from an antenna is an analog signal.
Digital Signal

Definition: A discrete waveform that takes discrete, finite amplitude values over time is known as a digital signal. The signaling technique that uses a digital signal is known as digital signaling. It’s also referred to as ON-OFF signaling.
Digital signals can be represented by a binary pattern consisting of ones (1s) and zeros (0s). It is also referred to as a non-continuous signal. Digital signals can also be decomposed into multiple sine waves known as harmonics.

The following image depicts the conversion of a digital signal into an analog signal using a DAC (Digital to Analog Converter). Similarly, an ADC is used to convert an analog signal into a digital signal.

Difference between Analog and Digital Signals
The following table summarizes the key differences between analog and digital signals:
| Feature | Analog Signal | Digital Signal |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Continuous wave that changes amplitude with respect to time. | Discrete wave that takes discrete values, such as a binary waveform, with respect to time. |
| Representation | Represented by a sine wave or similar continuous waveform (periodic or aperiodic). | Represented by square waves or similar shapes. |
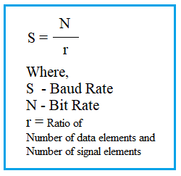
| Parameters | Amplitude, frequency (f) or time period (T), and phase (φ). (f=1/T) | Bit rate/bit interval, data rate, or baud rate. |
| Amplitude Values | Takes a continuous range of amplitude values (infinite number of possible values). | Takes a finite set of discrete values (e.g., binary: 1 and 0). |
| Noise Susceptibility | More prone to distortion or noise. | Less prone to distortion or noise. |
| Examples | Human voice captured by a microphone. EM signals transmitted from antenna. | Signals in computer buses, microcontroller buses, or microprocessor buses. Output of ADC. |
| Multimeter Functionality | Analog multimeters use a pointer on a scale. | Digital multimeters provide a numerical output. |
Conclusion
From the comparison between analog and digital signals, we can conclude that each type has specific applications. Analog signals are suitable for audio and video transmission, as well as EM wave transmission. Digital signals are used for DSP and microcontroller/microprocessor-based circuits. Digital signals are also used in image processing, telecommunication blocks, data compression, and more.
Advertisement
 RF
RF