PCM (Pulse Code Modulation): 5 Advantages and Disadvantages
Advertisement
This page explores the pros and cons of PCM (Pulse Code Modulation). It outlines the benefits and drawbacks of using this modulation technique.
What is PCM?
PCM stands for Pulse Code Modulation. In PCM, the analog speech waveform is sampled and directly converted into a multi-bit digital code by an Analog-to-Digital converter. This digital code is then stored in memory and later recalled for playback. Essentially, analog data is sampled and quantized before being represented in digital binary form. PCM converts continuous amplitude and continuous-time signal waveforms into discrete amplitude and discrete-time waveforms.
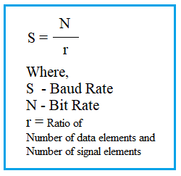
If you have an n-bit quantizer and a sampling rate of Fs, then the bit rate is:
- Rb (bits/sec) = n * Fs

In PCM, we represent each quantized level by a code number and transmit this code number instead of the sample value itself. The code number is in the form of a binary representation, and the digits of this binary representation are transmitted as pulses. In general, if M numbers 0, 1, … , M-1 are to be represented, then an N binary digit sequence KN-1_, … _K0 is required where M = 2.
In PCM, we are not compressing the signal m(t) itself, but its samples. DS0 carries a basic digital signaling rate of 64 kbps. A typical phone call’s audio sound is digitized at an 8 KHz sampling rate using 8-bit PCM.
Benefits (Advantages) of PCM
Here are the key benefits of using PCM:
- Robust against noise and interference: PCM signals are less susceptible to noise and interference compared to analog signals.
- Uniform transmission quality: PCM provides consistent signal quality throughout the transmission process.
- Efficient SNR and bandwidth trade-off: PCM allows for a good balance between signal-to-noise ratio and bandwidth usage.
- Secure data transmission: Digital encoding makes PCM data more secure.
- Efficient regeneration: PCM signals can be easily regenerated to eliminate accumulated noise.
- Easy to add or drop channels: Multiplexing and demultiplexing channels is simpler with PCM.
Drawbacks (Disadvantages) of PCM
Here are the main drawbacks of using PCM:
- Overload appears when the modulating signal changes: Overload can occur between samplings if the change is greater than the step size.
- Large bandwidth is required for transmission: PCM typically requires a wider bandwidth compared to other modulation techniques.
- Noise and crosstalk exhibit low attenuation but can rise: While generally robust, noise and crosstalk can still be a factor.
- An IDN (Integrated Digital Network) can only be realized by gradual extension of noise: Implementation within an IDN can be complex.
- Quantization error: The difference between the original analog signal and the translated digital signal is known as quantization error.
Advertisement
 RF
RF