Radar Frequency Bands Chart: A Complete Overview
Advertisement
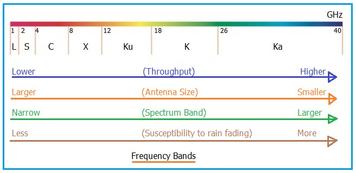
Radar systems utilize a variety of frequency bands, each with its own set of characteristics that impact performance factors like range and resolution. A radar frequency bands chart is a useful tool to categorize these frequencies, helping engineers select the most suitable band for their particular applications. Common radar frequency bands include L, S, C, X, Ku, and Ka bands.
Each band occupies a specific frequency range and is suited for different tasks. Most radars operate in the UHF and microwave frequency bands. Modern radars are even venturing into millimeter wave bands.
The table below provides an overview of various radar bands, including their frequency range, wavelength, maximum peak transmitted power, and typical applications.
| Radar Band | Frequency Range | Wavelength | Maximum Peak Power (MWatt) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HF | 3 to 30 MHz | 10 m to 100 m | - | Coastal radar systems, OTH (Over-the-Horizon) radar |
| P | 30 to 300 MHz | 1m to 10m | - | Applied retrospectively to early radar systems |
| UHF | 300 to 1000MHz | 0.3 to 1 m | 5.0 | Very long range, ground penetrating radar |
| L | 1 to 2 GHz | 15 cm to 30 cm | 30.0 | Long range air traffic control and surveillance |
| S | 2 to 4 GHz | 7.5 cm to 15 cm | 25.0 | Terminal air traffic control, long range weather or marine radar |
| C | 4 to 8 GHz | 3.75 cm to 7.5 cm | 15.0 | Satellite transponders, weather radar |
| X | 8 to 12 GHz | 2.5 cm to 3.75 cm | 10.0 | Missile guidance, marine and weather radar, ground surveillance |
| Ku | 12 to 18 GHz | 1.67 cm to 2.5 cm | 2.0 | High resolution mapping, satellite altimetry |
| K | 18 to 27 GHz | 1.11 to 1.67 cm | 0.6 | Used by meteorologists to detect clouds, used by police to detect motorists with high speed. |
| Ka | 27 to 40 GHz | 0.75 cm to 1.11 cm | 0.25 | Mapping, short range, airport surveillance |
| mm | 40 to 300 GHz | 1 mm to 7.5 mm | - | This millimeter band is used for various radar applications |
| Q | 40 to 60 GHz | 5 mm to 7.5 mm | - | Used for military communications |
| V | 50 to 75 GHz | 4 mm to 6 mm | - | Very strongly absorbed by atmosphere |
| W | 75 to 110 GHz | 2.7 mm to 4 mm | - | 76GHz LRR, 79GHz SRR automotive radar, high resolution meteorological observation, imaging |
Understanding the characteristics of each band empowers radar engineers to design systems optimized for specific environmental conditions and application requirements.
Conclusion
The radar frequency bands chart is a valuable resource for selecting the appropriate band for a given application, ensuring optimal radar performance across diverse scenarios.
Advertisement
 RF
RF