L, S, C, X, Ku, K, Ka Frequency Bands: Advantages and Disadvantages
Advertisement
This page provides a comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of the L, S, C, X, Ku, K, and Ka frequency bands. It’s designed to be a useful guide for understanding the trade-offs associated with each band.
Here’s a visual representation of these frequency bands:
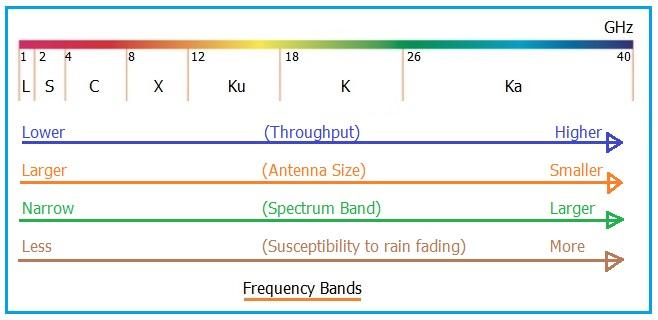
From the figure above, we can derive the following merits and demerits for each frequency band.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Band
L Band
Advantages:
- Less susceptible to rain fading.
- Cheaper equipment.
- Smaller antenna sizes.
Disadvantages:
- Very small bandwidth allocated for L-band in Inmarsat (1.3 to 1.7 GHz).
- Costly spectrum due to scarcity.
S Band
Advantages:
- Less susceptible to rain fading compared to Ku and Ka bands.
Disadvantages:
- Supports lower throughput.
- Narrow bandwidth.
- Larger antenna sizes.
C Band
Advantages:
- Wider and global coverage.
- Lower propagation delay.
- Less attenuation compared to other bands.
Disadvantages:
- Large antenna size.
- Lower throughput compared to other bands.
X Band
Advantages:
- Less interference from rain fading compared to higher frequency bands like Ku and Ka (rain fading is dominant above 10 GHz).
- Supports smaller antennas.
- Can handle higher power.
- Supports detection of smaller particles in radar applications.
- Lower cost equipment.
Disadvantages:
- More attenuation due to rain, snow, and ice.
- Limited clear air measurements in radar.
Ku Band
Advantages:
- Smaller antenna size.
- Provides wider beam coverage compared to other bands.
- Higher throughput compared to lower bands, though less than Ka band.
Disadvantages:
- Suffers from rain fading due to absorption of EM waves by water droplets (more than C band).
K Band
Advantages:
- Supports high throughput compared to Ku band.
- Supports smaller antennas compared to Ku band.
- Less susceptible to rain fading compared to Ka band.
Disadvantages:
- High atmospheric attenuation, unsuitable for long-distance communication.
- More susceptible to rain attenuation compared to Ku band.
Ka Band
Advantages:
- Provides high throughput beams.
- Delivers high bandwidth communication.
- Provides high power for transmission.
- Smaller equipment, easy to install and maintain.
- Transmits higher data over the same bandwidth compared to Ku band.
Disadvantages:
- Suffers from rain fading due to absorption of higher frequency EM waves by water droplets.
- Higher propagation delay due to double hop.
Advertisement
 RF
RF