DMR Radio Basics: Digital Mobile Radio Tutorial
Advertisement
This tutorial covers the basics of the DMR (Digital Mobile Radio) system. It outlines the features of DMR radio, including DMR network architecture, DMR air interface, DMR channel types, and the advantages of DMR (Digital Mobile Radio). There are three different DMR Tiers: DMR Tier-I, DMR Tier-II, and DMR Tier-III. These tiers are categorized by their frequency of operation, transmit power, and typical applications.
Features of DMR - Digital Mobile Radio
The following table outlines the key features of DMR (Digital Mobile Radio):
| Specifications | DMR Radio |
|---|---|
| Radio Technology type | Digital |
| Frequency of operation | 446 MHz for DMR Tier-I 66 to 960 MHz for DMR Tier-II and Tier-III |
| Frequency Channel Bandwidth | 12.5 KHz |
| Number of time slots | 2 |
| Access Technique | • FDMA (one band for uplink and another for downlink), 1 pair of frequencies used for Tx/Rx direction. • TDMA (2 time slots per channel) |
| Traffic type | Both voice calls and data calls are supported |
| Modulation Scheme | 4 state FSK, 4 possible symbols, 4800 symbols/sec, 9600 bits/sec, |
DMR Air Interface | DMR Channel Types
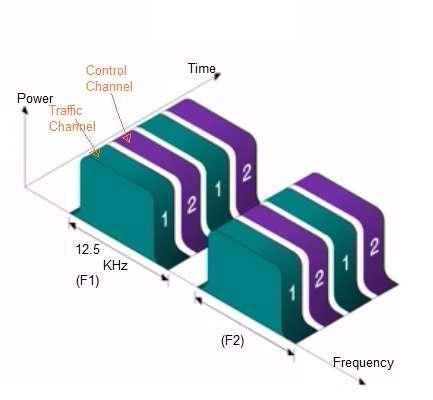
Figure 1 depicts the DMR Air interface. There are two frequency bands: the uplink band and the downlink band. In both bands, each channel consists of 12.5 KHz bandwidth. Each channel is further divided into two different time slots using TDMA. These slots are known as logical channels, while the frequency is the physical channel. Hence, there are two logical channels per physical channel.
In each physical channel, one logical channel is used for traffic and the other for control information. The traffic channel carries either voice or data. The control channel is used for various functions such as managing and controlling subscriber unit registration, call requests, and channel assignments. It periodically broadcasts useful system-related information to DMR portable subscriber units. The control channel can also transmit short data messages in emergency situations.
Therefore, DMR channels are of two types: physical (frequency) and logical (time slots). The logical channel can be further categorized into traffic and control channels based on the information it carries.
DMR Network Architecture

Figure 2 depicts the DMR network architecture. As shown, DMR consists of two main elements: the base station and portable subscriber radio units. The area covered by DMR technology is divided into cell sites. Each cell site consists of one or more base stations (BSs). Each base station can interface with a LAN using IP switches or with a WAN using routers. Network gateways are often used to connect with PSTN/PBX, providing connectivity with analog and digital telephone systems.
Benefits or Advantages of DMR (Digital Mobile Radio)
The following are the benefits or advantages of DMR (Digital Mobile Radio):
- DMR is an open standard, meaning a portable DMR handset from one manufacturer can work with a base station from another manufacturer and vice versa. Moreover, portable handsets from different manufacturers can communicate and interoperate.
- DMR provides digital quality audio, eliminating external noise and offering better audio quality, even at the cell edge.
- It offers double capacity due to the use of two time slots per channel with TDMA.
- Migration is easy, as DMR supports both analog and digital modes.
- DMR handsets have longer battery life.
- DMR supports Caller ID, making the caller’s identity visible to all recipients.
- DMR offers secure communication through encryption. Keys are exchanged before communication begins to encrypt voice/data over the channel.
- DMR has numerous applications, including remote monitoring (telemetry), SCADA, vehicle automation, and GPS.
DMR Tutorial References
Read ETSI standards for more information on DMR (Digital Mobile Radio):
- TS 102 361-1: Air interface protocol
- TS 102 361-2: Voice and Other services
- TS 102 361-3: Data protocol
- TS 102 361-4: Trunking protocol
Advertisement
 RF
RF
