Receiver Minimum Input Sensitivity in WiFi 7 (IEEE 802.11be)
Minimum input sensitivity is the lowest power level a receiver needs to decode a signal successfully in Wi-Fi 7. It impacts range, performance in noisy environments, and power efficiency.
Showing 20 posts (Page 4 of 5)
Advertisement
Minimum input sensitivity is the lowest power level a receiver needs to decode a signal successfully in Wi-Fi 7. It impacts range, performance in noisy environments, and power efficiency.
Explore key RF antenna parameters, measurement methods, and tuning strategies to optimize antenna design and maximize efficiency in wireless communication systems.

Explore RF comb generators for EMC/RFI testing, their function, applications in frequency synthesis, and key specifications. Learn how they aid in electromagnetic compatibility assessments.

Explore RF filter testing methods and essential measurements like insertion loss, return loss, and bandwidth using test equipment like VNAs and spectrum analyzers.

Understand RF gain flatness measurement: formula, test setup with signal generators and spectrum analyzers, and step-by-step procedures for accurate results.

Learn how to measure RF harmonic distortion using test equipment like spectrum analyzers and signal generators to ensure system linearity.

Learn to measure RF intermodulation distortion (IMD) using a two-tone test setup. Understand the equipment, procedure, and importance of IMD measurements.

Learn how to measure RF phase noise using a spectrum analyzer, including test setup, procedure, and key considerations for optimizing oscillator performance.

Test setup and procedure for verifying the maximum tolerable power of an RF receiver without affecting its functionality.

Learn how to accurately measure RF receiver sensitivity using standard test equipment. This guide covers test setup, procedure, and sensitivity considerations.

Learn about RF synthesizer settling time, its importance in transceivers like Bluetooth chips, and methods for its measurement using power vs. time or frequency vs. time analysis.

Explore RF wafer probe testing, on-wafer measurements, and specialized equipment for characterizing RF and microwave devices on semiconductor wafers, including VNAs and spectrum analyzers.
Explanation of RSCP, Ec/Io, and CQI parameters in 3G UMTS networks, detailing their purpose, measurement, and application in assessing signal quality and network performance.
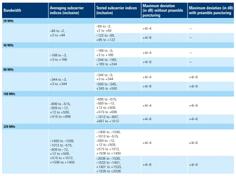
An overview of spectral flatness in Wi-Fi 7, focusing on its importance in ensuring uniform power distribution across the channel bandwidth and maintaining signal integrity.
Transmit power accuracy and RSSI measurement are critical in WiFi 7 for reliable wireless communication, performance optimization, and interference management.
A guide to diagnosing and resolving modulation spectrum failures in wireless devices, covering filter issues and local oscillator leakage.
Explore BER (Bit Error Rate) and BLER (Block Error Rate) in 3G UMTS networks, specifically HSPA, and their importance in assessing data transmission quality.
Explore BER, BLER, and DBLER metrics in GSM/GPRS systems, including limits, measurement, and associated testing equipment for performance evaluation.
Dropped Call Rate (DCR) in GSM is a key metric indicating the percentage of unexpectedly terminated calls. Monitoring and reducing DCR enhances network reliability and user satisfaction.
Explore handover latency and success rate in GSM: key metrics ensuring seamless call continuity during cell transitions, impacting user experience and network stability.
Advertisement