LOS vs NLOS: Understanding Line of Sight in Wireless Communication
Advertisement
This article compares wireless LOS (Line of Sight) and NLOS (Non-Line of Sight) channels, highlighting their key differences. We’ll also touch upon various wireless channel models.
LOS: Line of Sight Channel

As mentioned, LOS stands for Line of Sight. Figure 1 (above) depicts line of sight communication between two transceivers. This LOS deployment is possible when there is no obstruction between the base station (BS) and mobile/fixed subscriber stations (SSs).
In simpler terms, LOS communication occurs when there is a clear, unobstructed path between the transmitter and the receiver. Due to the reduced attenuation in LOS communication, it offers better signal strength and higher throughput compared to its NLOS counterpart.
Examples of LOS wireless links:
- Microwave point-to-point communication
- Point-to-point connection between a BS and an SS
NLOS: Non-Line of Sight Channel

NLOS stands for Non-Line of Sight. Figure 2 (above) illustrates a NLOS deployment scenario.
As shown, a wireless link is considered NLOS when natural and/or man-made structures block the direct path between the base station and subscriber stations.
Essentially, NLOS communication is possible even when there is an obstruction between the transmitter and the receiver. The signal arrives at the receiver after navigating through various obstacles. Along its path, the signal undergoes attenuation, reflection, diffraction, and penetration.
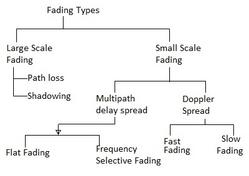
In the NLOS case, a wireless link can only be established if a reflective path exists between the base station and the subscriber station, as depicted in the figure. Due to the NLOS environment, multiple copies of the signal arrive at the receiver at different times and with varying amplitudes. This phenomenon results in Inter-Symbol Interference (ISI) and Inter-Carrier Interference (ICI).
This problem is often mitigated using OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing) and OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access) techniques in conjunction with a cyclic prefix. The length of the cyclic prefix is carefully chosen to be greater than the delay spread value to effectively overcome ISI/ICI.
OFDM/OFDMA techniques have become widely adopted and are employed in numerous modern wireless communication systems such as WiMAX, WLAN, LTE, LTE-Advanced, and others.
Examples of NLOS wireless links:
- Wireless connection between a BS (Base Station) and an SS (Subscriber Station) / MSS (Mobile Subscriber Station)
Advertisement
 RF
RF