RF vs. Microwave: Key Differences Explained
Advertisement
The comparison between RF (Radio Frequency) and Microwave technologies often surfaces when discussing frequency spectrum management. While RF covers a broad spectrum from 3 kHz to 300 GHz, Microwave is a subset within this range, typically spanning from 300 MHz to 300 GHz.
This guide explores the distinctions between RF and Microwave, focusing on their applications and unique characteristics. Both RF and Microwave are used to represent frequency ranges in the electromagnetic spectrum and have many similar, as well as different, applications. RF is the abbreviation for ‘Radio Frequency’ signal.
The following table outlines the frequency and wavelength ranges for both RF and Microwave:
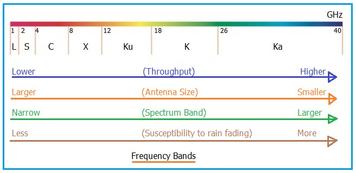
RF (Radio Frequency) EM spectrum has been classified into eight regions based on radiation intensity. The major divisions are into radio spectrum and optical spectrum. Radio spectrum covers radio waves, microwaves and terahertz radiations. Optical spectrum covers infrared, visible, ultra violet, X-rays and gamma radiations. Radio waves range from 3 KHz to 300 GHz. Hence RF starts from much lower than the microwave starting range as mentioned below. In radio waves antenna wavelength varies from hundreds of meters to about 1 millimeter.
Microwave
The term “micro” signifies something very small, essentially a millionth part of a unit. The term “Microwave” is used to identify EM waves above 1 GHz in frequency because of the short physical wavelength of these frequencies. Microwaves are essentially radio frequency (RF) waves. However, a difference between RF and microwave exists as far as operating range and applications are concerned. Microwaves range from 300MHz to 300GHz.
Most microwave applications range up to 100 GHz. The unique features of microwaves include:
- High antenna gain and directivity
- Large Bandwidth
- It travels by LOS (Line Of Sight)
- Low noise level in the 1-10 GHz range, allowing for the easy detection of very low signals at the receiver
- Microwaves penetrate the ionosphere with less attenuation and distortion
Difference Between RF and Microwave
Although engineers often use the terms RF and Microwave interchangeably, there are slight distinctions between them, as highlighted below. While the starting range of microwaves can be ambiguous, it generally starts from 1 GHz and spans up to 1 Tera-Hertz. This corresponds to wavelengths ranging from 30 cm to 0.3 mm.
| Specifications | RF | Microwave |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency range (Hz) | 3 KHz to 300 GHz | 300 MHz to 300 GHz (Subset of RF) |
| Wavelength | Longer wavelength, 1 mm to 100 Km | Shorter wavelengths, 1 mm to 1 m |
| Signal Behavior | Longer range, less prone to attenuation | Shorter range, more susceptible to losses |
| Propagation | Easily propagates through obstacles like walls | Requires line of sight; higher attenuation |
| Power Levels | Lower power for communication systems | Higher power for applications like radar |
| Transmission Medium | Works well with both guided and unguided media | Primarily guided media (e.g., waveguides) |
| Components | RF amplifiers, antennas, modulators | Waveguides, magnetrons, circulators |
| Bandwidth | Typically narrower | Wider bandwidth, supports high data rates |
| Energy Density | Lower energy density | Higher energy density |
| Applications | Mobile, AM/FM radio, television | radar, satellite and space communication |
Conclusion
The primary difference between RF and Microwave lies in their frequency ranges and applications. RF encompasses a broader spectrum, including microwaves, and is widely used for long-range, low-power communication. Microwaves are a higher frequency subset of RF, suitable for short-range, high data rate applications like radar and satellite systems.
Advertisement
 RF
RF