Understanding Delay Spread and Doppler Spread
Advertisement
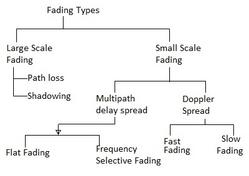
This page describes Delay Spread and Doppler Spread.
Delay Spread
As we know, a radio frequency signal takes different paths to reach its destination due to multipath propagation. This multipath propagation causes reflection, refraction, and scattering of the radio signal. Hence, when a signal is transmitted from one place to another, multiple copies of the signal are received with different amplitudes and different delays (leading to different times of arrival) at the receiver.
For example, if an impulse is transmitted, it will no longer be an impulse when it is received at the other end. Instead, it will become a pulse with a spreading effect. The effect that causes this spreading of the signal is known as Delay Spread.
To measure the performance of a wireless system, different scenarios, ranging from low to medium to high delay spreads, are considered for testing purposes.
Delay spread helps determine the coherence bandwidth and coherence time of a wireless system.
Doppler Spread
The Doppler frequency shift is usually different from path to path when a signal arrives at the wireless receiver.
Hence, the transmitted signal frequency will experience Doppler spreading and is seen as spectral widening or broadening in the received signal power spectrum. The width of this spectrum is known as Doppler Spread or fading bandwidth.

Doppler Spread is also known as the fading rate.
Advertisement
 RF
RF