Doppler Spread vs. Coherence Time in Wireless Communication
Advertisement
This article explains the difference between Doppler spread and coherence time, two important concepts for understanding the characteristics of wireless channels. Both are related to how the channel changes over time, affecting the quality of signal transmission.
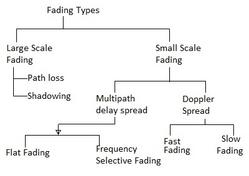
Doppler Spread
- Doppler shift refers to the random changes in a channel that occur due to the mobility of a user. Imagine a mobile phone user moving – this movement introduces variations in the received signal.
- Doppler spread describes the effect of shifting or spreading the frequency components of a signal. Essentially, the movement causes a “smearing” of the signal’s frequency.
- It’s caused by time selective fading. In other words, for short periods of time, the channel behaves like a fading channel, while for the rest of the time it behaves like a flat channel.
- Based on the Doppler spread, fading can be classified as either fast fading or slow fading:
- Fast Fading: The channel impulse response changes rapidly within the duration of a single symbol being transmitted. Think of it as the channel changing drastically while a single piece of data is being sent.
- Slow Fading: The channel impulse response changes much slower than the rate at which symbols are transmitted. This means the channel stays relatively stable during the transmission of multiple symbols.
- Doppler spread is expressed as the maximum Doppler shift (fm).

Coherence Time
- The coherence time of a channel is the inverse of the Doppler spread.
- It represents the speed at which the channel characteristics change over time.
- This value determines how quickly fading occurs in the channel.
- If channel changes are faster than the modulated symbol rate, we see fast fading_. On the other hand, if channel changes are _slower than the symbol rate, slow fading occurs.
- Coherence time is expressed as follows:

Advertisement
 RF
RF