
Understanding Substrate Integrated Waveguides (SIW)
Learn about Substrate Integrated Waveguides (SIW), their structure, dominant mode (TE10), benefits like high power handling and low radiation losses, and applications in RF and 5G.
Advertisement

Learn about Substrate Integrated Waveguides (SIW), their structure, dominant mode (TE10), benefits like high power handling and low radiation losses, and applications in RF and 5G.

Explore the 60 GHz frequency band, its high-speed wireless capabilities, key applications, and challenges like limited range and environmental factors.

Explore the key differences between EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) and EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility). Learn about sources, types, testing, and why both are crucial for reliable electronic systems.

Explore the electromagnetic spectrum: frequencies, wavelengths, sources, and applications of EM waves, including radio, microwave, infrared, visible light, and more.

Explore the RF front end's function in wireless systems, including its key components like antennas, filters, LNAs, and PAs. Learn about RF front end manufacturers.
This article defines VSWR, explains return loss, and clarifies the relationship between VSWR and return loss in transmission lines.
Explore the concept of wave impedance, defined as the ratio of electric to magnetic fields in electromagnetic wave propagation. Learn about field dominance and related RF concepts.

Explore the fundamental differences between uplink and downlink in wireless networks, including examples in GSM and satellite communication, frequencies, and technical components.

Understand the core differences between UPS and inverters, including function, backup time, application, and price. Learn which is best for your needs.

Learn about VHF, UHF, and microwave repeaters, how they work, and their use in extending communication range for various wireless applications.
Explore the fundamental differences between voltage and current in electronics, including their definitions, measurement units, and relationships to resistance (Ohm's Law).

Explore the distinctions between waveguides and coaxial lines, covering their functions, modes, advantages, and disadvantages in electromagnetic wave transmission.

Explore the relationship between wavelength and frequency in electromagnetic waves, their impact on antenna size, and the influence of the dielectric constant.

Explore the key differences between white noise and colored noise, their spectral characteristics, and how to generate them using MATLAB.

Understand the core differences between wires and cables, including composition, protection, and application. Learn about various cable types like twisted pair and coaxial.

Explore the three primary modes of wireless propagation: ground wave, sky wave, and line-of-sight, outlining their characteristics and typical applications.
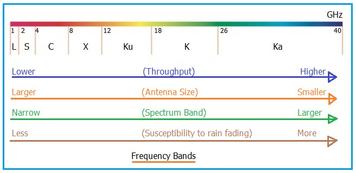
Explore X band frequency characteristics, including its range (8-12 GHz), advantages like lower rain fade and noise, and applications in satellite communication and meteorology.
Explore the key differences between X-Ray and millimeter wave (mm-wave) technologies, including their wavelengths, frequencies, applications, advantages, and disadvantages.

Explore the distinctions between X-rays and gamma rays: origins, energy levels, applications, advantages, and disadvantages. Crucial for imaging, diagnostics, and cancer treatment.

Understand the Zero IF transceiver architecture, its advantages, disadvantages, and applications in RF communication systems.
Advertisement