X Band Frequency: Values, Advantages, and Applications
Advertisement
This page details X Band frequency values, applications, and advantages.
Frequency Band Designations
| Frequency Band | Frequency Range | Wavelength |
|---|---|---|
| X Band | 8 to 12 GHz | 3.8 to 2.5 cm |
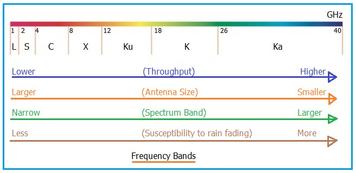
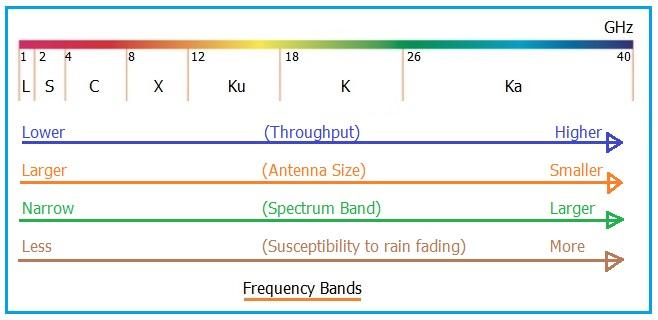
The X band frequency sits between the C Band and Ku Band, as shown in the figure below.
As shown in the table, the X band ranges from 8 GHz to 12 GHz in the frequency spectrum, with corresponding wavelengths between 2.5 centimeters and 3.8 centimeters. It falls under the SHF (Super High Frequency) category in the EM (Electromagnetic) spectrum. Within the 8 to 12 GHz band, the 8.175 to 8.4 GHz range is allocated for various communication applications, as detailed further below. A Radio Frequency (RF) center frequency of approximately 8.2 GHz is commonly used for these applications.
X Band Frequency Advantages
Here are the advantages of the X Band frequency compared to other frequency bands:
- Rain fading becomes significant at radio frequencies above 10 GHz. The X Band, being mostly below this threshold, experiences less interference from rain fading compared to higher-frequency bands like Ku band and Ka band.
- It has lower noise, making it a reliable choice for high data and low noise data communications.
- X band performs better with smaller antennas and can handle higher power.
X Band Frequency Applications
The following are common applications of the X Band Frequency:
- Used in satellites for Earth exploration.
- Used in both fixed and mobile satellites for communications from Earth to space (uplink).
- Used in meteorological satellites for monitoring weather conditions, utilizing frequencies from 8.175 GHz to 8.215 GHz for this specific purpose.
Advertisement
 RF
RF