Missile Seeker Radars: Pulse vs. FMCW Comparison
Advertisement
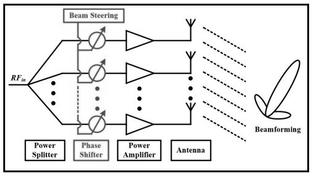
Missile seeker radars are crucial for missile guidance and target acquisition, especially in the final stages of an attack. These systems usually operate at millimeter wave frequencies, enabling precision guidance. The use of millimeter waveforms offers several advantages, including a broad bandwidth, reduced interference from environmental factors like smoke, fog, and dust, and enhanced spatial resolution.
Here’s a breakdown of how missile seeker radars function during combat:
- Scanning and Target Acquisition: The radars scan the designated area to locate potential targets.
- Target Lock: Once a target is identified within the radar’s field of view, the radar antenna locks onto it.
- Tracking and Interception: The missile then continuously tracks the target, ensuring a successful hit.
In scenarios where concealing the radar’s location from the enemy is vital, a passive radiometer sensor can be employed instead of the active radar. This radiometer tracks the target by detecting and analyzing the thermal emissions it produces through a conical scanning motion.
Pulse Radar
Pulse radars are designed with a wide receiver bandwidth to capture a significant portion of the pulse’s spectral components. This allows for accurate detection of each radar pulse without distorting its shape, hence the name “pulse radar.”
For a more in-depth understanding, refer to a radar tutorial that includes a pulse radar block diagram.
FMCW Radar
FMCW (Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave) radars use radio frequency signals that are frequency-modulated with a linear sweep. This sweep is typically achieved using either a triangular or sinusoidal modulating waveform.
For more detailed information, explore resources on FMCW radar systems, which provide explanations alongside relevant equations.
Pulse vs. FMCW Radar: Key Differences
The following table highlights the differences between pulse radar and FMCW radar systems used in missile seeker applications, operating at frequencies of 35GHz and 94GHz.
| Missile Seeker radar specifications | Pulse Radar (35GHz) | Pulse Radar (94GHz) | FMCW Radar (35GHz) | FMCW Radar (94GHz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average transmission power | 10mW | 5mW | 100mW | 50mW |
| Peak transmission power | 2W | 1W | - | - |
| Transmission Bandwidth | 300MHz | 300MHz | 500MHz | 500MHz |
| Receiver IF Bandwidth | 300MHz | 300MHz | 200MHz | 200MHz |
| Antenna Diameter | 16.25 cm | 16.25 cm | 16.25 cm | 16.25 cm |
| Antenna Efficiency | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Antenna Beamwidth | 3.6 Degree | 1.3 Degree | 3.6 Degree | 1.3 Degree |
| Pulse width of transmitted waveform | 0.1 sec | 0.1 sec | - | - |
| Pulse repetition frequency | 50 KHz | 50 KHz | - | - |
| Target RCS | 50 m2 | 50 m2 | 50 m2 | 50 m2 |
| Scanning Loss | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Noise figure of receiver | 9dB | 12dB | 9dB | 12dB |
| Integration Time | 500 msec | 70 msec | 500 msec | 70 msec |
Advertisement
 RF
RF