Radar Terminology Explained: Key Concepts and Definitions
Advertisement
This tutorial section covers radar basics, including terminology, measurements, Doppler radar, FMCW radar, radar bands, radar scopes, weather radar, ground radar, and range/resolution.
Radar Terminology
This page describes terms related to radar, including frequency, phase, bandwidth, wavelength, pulse width, PRF, PRT, duty factor, beam width, Radar Reflectivity Factor (dBZ), bistatic radar, monostatic radar, 3D radar, and 2D radar.
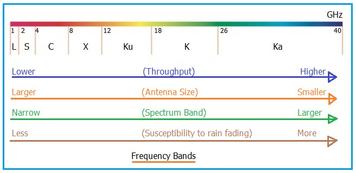
Frequency
Frequency refers to the total number of completed cycles per second. It’s expressed in Hertz (Hz).
Phase
Phase refers to the phase of an electromagnetic (EM) wave and represents a fraction of a full wavelength. It’s measured in radians or degrees.
Bandwidth
Bandwidth is the frequency difference between the upper and lower frequencies on the EM spectrum radiation. It’s expressed in Hz.
Wavelength
Wavelength is the distance from wave crest to wave crest along the direction of travel of an EM wave. The unit is typically centimeters.
Pulse Width
Pulse width is the time interval between the leading and trailing edges of a pulse at a point where their amplitudes are 50% of their maximum values. The unit is microseconds (µs).
PRF
PRF refers to Pulse Repetition Frequency, which is the number of peak power pulses transmitted per second.
PRT
PRT refers to Pulse Repetition Time. It’s the time interval between two peak pulses.
Duty Factor
Duty factor is the amount of time a radar transmits compared to its listening time. It’s often expressed as a percentage. It can be calculated by multiplying PRF and pulse width or by dividing pulse width by PRT.
Beam Width
Beam width is the angle between the 3dB half-power points on the main lobe, with reference to the peak effective radiated power used on the main lobe. The unit is degrees.
Radar Reflectivity Factor (dBZ)
dBZ is the logarithmic scale for measuring Radar reflectivity factor.
This dBZ value, calculated using the above equation, is what we usually see displayed on a radar screen or on imagery downloaded from a website. Some of the transmitted power is likely to be returned to the radar antenna as a result of backscattering. Reflectivity is basically a measure of how much power was scattered back to the radar from the target. Stronger targets will have higher levels of reflectivity and hence return more energy. Therefore, stronger targets have higher reflectivity values, i.e., higher dBZ levels. dBZ is also related to the number of drops per unit volume and the sixth power of their diameter.
Bistatic Radar
Bistatic radar has two antennas: one for transmission and the other for reception. These antennas can be located side by side or far away from each other.
Monostatic Radar
Monostatic radar is a radar that uses a common antenna for both transmission and reception or uses two adjacent antennas for the same purpose. Doppler weather radars are typically of this type.
2D Radar
2D radar, or two-dimensional radar, provides azimuth and range information.
3D Radar
3D radar produces three-dimensional position data of the target. It covers range, azimuth, and height.
Advertisement
 RF
RF