ATM vs TDM: Key Differences Explained
Advertisement
This page compares ATM and TDM and mentions the difference between ATM and TDM. As we know, ATM stands for Asynchronous Transfer Mode, and TDM stands for Time Division Multiplexing.
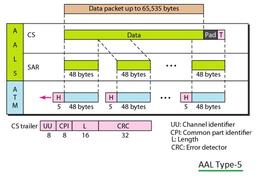
ATM-Asynchronous Transfer Mode

Fig-1: ATM-Asynchronous Transfer Mode
- ATM operates on cells.
- It multiplexes or combines cells, similar to TDM operation.
- However, it has a fixed cell size of 53 bytes. This 53 bytes is divided into 5 bytes of header and 48 bytes of payload containing information.
- It has a basic transmission rate equal to 149.76 Mbps, which is equal to the STM-1 rate of the SDH hierarchy of transmission.
- It incorporates a minimal amount of error detection and flow control. Error control is provided for the header part using the HEC (Header Error Control) field. It is not provided for the payload or information part; the same should be taken care of by end terminal equipment.
- As the information field is fixed and has a smaller size, this results in minimum packet delay.
- It has a policing function. Hence, the digit transmission rate is restricted below the required rate limit.
TDM-Time Division Multiplexing

Fig-2: TDM-Time Division Multiplexing
Figure 2 depicts TDD and TDMA utilizing frequency resource sharing in LTE and GSM systems consecutively using the TDM concept. As shown, LTE uses frequency-f1 between the UE and eNodeB at different time slots 0 to 10. This type of LTE frame is referred to as an LTE-TDD frame.
As shown, GSM uses the same frequency channel 124 at different time slots TS0 to TS7 for communication between the GSM base station and subscriber stations.
- TDM operates on packets. The frame transmission and reception follows the TDM concept, wherein various fields are arranged in a TDM fashion one after the other consecutively.
- The packet length in TDM is variable and depends on the configuration.
- It multiplexes or combines packets irrespective of technology. Hence, it is used in different technologies in order to utilize frequency resources efficiently. For example, the same frequency is assigned to multiple users on a time-shared basis.
- It does not incorporate error detection and flow control; it is the duty of parent technologies utilizing the TDM service to take care of the same.
- The rate limit depends on the number of packets transmitted over some time duration, and it depends on the clock.
Advertisement
 RF
RF