
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) Tutorial
Learn the basics of Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) in computer networks, covering architecture, cell format, protocol layers, addressing, and services.
Showing 10 posts (Page 1 of 1)
Advertisement

Learn the basics of Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) in computer networks, covering architecture, cell format, protocol layers, addressing, and services.

Explore the advantages and disadvantages of Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) technology, including its traffic support, overhead, and cost implications.
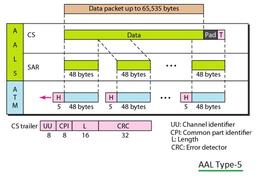
Explore the different ATM Adaptation Layers (AALs): AAL1, AAL2, AAL3/4, and AAL5. Understand their characteristics, sublayers (CS & SAR), and suitability for various ATM service classes.

Explore ATM call signaling with a focus on PNNI and UNI protocols. Learn about message flow, call setup, maintenance, and teardown in ATM networks.

Explore the key differences between ATM and STM, including multiplexing techniques, bandwidth allocation, overhead, and suitability for bursty traffic.

Explore the differences between Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) and Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) in this comprehensive comparison.
A comparison of ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) and Frame Relay networks, covering their application, data handling, QoS support, and more.

Compare Switched Virtual Circuits (SVCs) and Permanent Virtual Circuits (PVCs) in ATM/Frame Relay networks. Explore their differences in connection type, setup, usage, and cost.

Explore the differences between ATM service categories like CBR, VBR, ABR, UBR, and GFR. Learn how each handles data traffic for optimal network performance.

Explore the functions of ATM switches, their role in cell switching, how they work, and how they handle operations like VP/VC mapping and congestion control.
Advertisement