Active vs. Passive Hubs in Computer Networks
Advertisement
Hubs are essential devices used to connect multiple computers or network devices in a network. They come in two main types: active and passive hubs, each serving distinct roles in maintaining and transmitting data signals across the network.
In this article, we’ll explore the differences between active and passive hubs, including their advantages and disadvantages.
What is a Hub?
A hub is a network device that connects multiple nodes or PCs through its ports or connections using twisted-pair or optical cables. It operates on Layer 1 of the OSI model, which is the physical layer.
An Ethernet hub doesn’t manage the traffic passing through it. It simply broadcasts the packet out to all ports except the port of entry. Hubs are available in various port configurations, such as 4, 5, 8, 12, and so on.
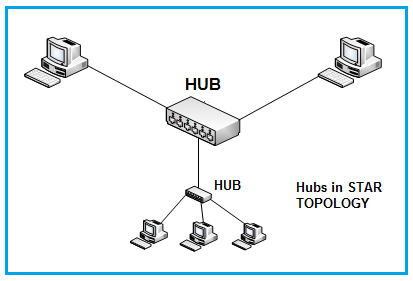
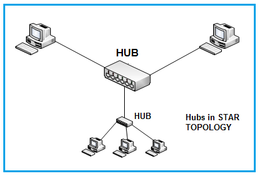
Figure 1: A hub used to interface various nodes or PCs in a star configuration.
The Ethernet hub organizes cables and relays signals to the other media segments. It can also be used in other configurations based on how packets travel between nodes.
The types of hubs are mainly categorized into Active Hub, Passive Hub, and Intelligent Hub. Let’s understand active and passive hubs and differentiate them.
Active Hub
An active hub is a network device that amplifies or regenerates the electrical signal before forwarding it to other connected devices. This helps in extending the distance of the network and maintaining signal strength and integrity. Active hubs require external power sources and are often used in larger networks where signal loss over long distances is a concern.
Advantages of Active Hubs
- It helps in extending the distance between two nodes.
Disadvantages of Active Hubs
- It amplifies noise in addition to the desired signals.
- They are more expensive compared to passive hubs.
- It requires a power supply.
Passive Hub
A passive hub simply serves as a conduit for the data signals without amplification or regeneration. It transmits the signal to the other devices as received, which makes it suitable for short-distance connections. Passive hubs do not require any external power source and are used in smaller networks where signal strength is not a major concern.
Advantages of Passive Hubs
- Passive hubs are cheaper compared to active hubs.
- It does not amplify noise.
- It does not require a power supply.
Disadvantages of Passive Hubs
- It reduces cable distance by half as it does not amplify or boost the signals.
- It is only used to share the physical medium.
Active Hub vs. Passive Hub
The following table summarizes the differences between active and passive hubs used in computer networks:
| Parameter | Active Hub | Passive Hub |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Regenerates and amplifies the signal | Simply transmits the signal as received |
| Signal strength | Maintains and boosts signal strength | Does not maintain signal strength |
| Power source | Requires an external power source | Does not require an external power source |
| Network size | Suitable for larger networks | Suitable for smaller networks |
| Distance coverage | Can cover larger distances due to amplification | Limited distance coverage |
| Complexity | More complex with additional circuitry | Simpler design with fewer components |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | Usually less expensive |
| Applications | Used in networks requiring signal boosting | Used in networks where signal strength is not an issue |
| Examples | Ethernet hubs with amplification capability | Basic hubs without any signal processing |
Summary
Active hubs amplify and maintain signal strength for extended distances, making them suitable for larger networks, while passive hubs simply transmit signals as received, making them ideal for smaller networks. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the right hub based on network size and requirements.
Advertisement
 RF
RF