Ethernet Hub Types: Passive, Active, and Intelligent Hubs
Advertisement
This page covers the basics of ethernet hubs and their different types. We’ll explore passive hubs, active hubs, and intelligent hubs.
Introduction
A hub is a networking device that connects multiple ethernet devices using twisted pair or fiber optic technology. This allows these devices to operate as a single network segment within a larger network or the internet.
Hubs operate at Layer 1, the Physical Layer, of the OSI protocol stack. Essentially, they function as a multiport repeater. In a hub-based Ethernet network, only one device can transmit data at a time. Each host is responsible for collision detection and retransmission of packets.
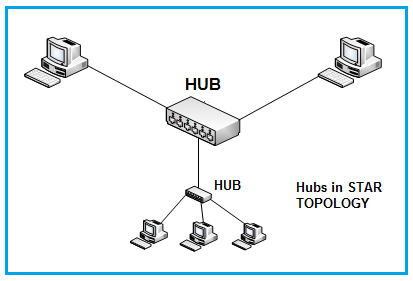
In simple terms, an ethernet hub is a box with connectors for PCs or nodes. Like repeaters, hubs regenerate signals bit by bit as they travel through the physical medium, allowing signals to reach greater distances. Furthermore, a hub can share the same signal to a group of nodes. The connection points are called ports. Figure 1 depicts a hub in a star configuration. Various other configurations are also supported, such as ring, bus, and tree, depending on how the signal is passed from one node to others.
Ethernet Hub Basics | Types of Hubs
The following sections describe the basics of ethernet hubs and the different types available:
Passive Hub
- This type of hub does not amplify or boost the signal.
- It does not manipulate or view the traffic passing through it.
- Passive hubs do not require electrical power to operate.
Active Hub
- It amplifies the incoming signal before passing it on to other ports.
- It requires AC power to function.
Intelligent Hub
- Also known as smart hubs.
- Functions as an active hub and includes diagnostic capabilities.
- Intelligent hubs include a microprocessor chip and are very useful in troubleshooting network issues.
A hub is also called a concentrator because it serves as a central connection point for an Ethernet Local Area Network. Ethernet hubs are available with different numbers of ports, such as 4, 5, 8, or 16 ports. You can choose a hub based on your connectivity requirements. The ports can connect ethernet cables supporting various speeds like 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps, depending on the hub’s capabilities.
Advertisement
 RF
RF

