GSM: Key Features and Benefits in Mobile Communication
Advertisement
Introduction
GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) is a widely adopted standard for mobile communication that transformed the way we connect globally. It provides seamless voice, text, and data communication, enabling users to stay connected across borders. This guide explores the key features and benefits of GSM, highlighting its role in shaping modern wireless networks.
Cellular communication is in use throughout the world, and GSM is the technology behind it. It’s primarily used for mobile-to-mobile communication for voice and data applications, including SMS, MMS, Email, and web browsing. GSM stands for Global System for Mobile Communication.
Let’s understand how GSM works with the help of the following figure:
When Mobile 1 wants to talk to Mobile 2, Mobile 1 dials Mobile 2’s number. This call request is forwarded to the Base Station through a signaling channel. The Base Station checks if Mobile 2 is available. If Mobile 2 is not in use, the Base Station sends a ringing tone to it. Once Mobile 2 accepts the call, a connection is established between both mobiles. A dedicated frequency/time slot is used for this connection until the call ends. Hence, FTDMA (Frequency Time Division Multiple Access) is the access scheme used in GSM.

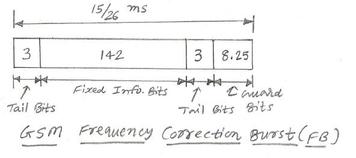
GSM uses the 890-915 MHz frequency band for communication from Mobile 1 to the Base Station and the 935-960 MHz frequency band from the Base Station to Mobile 2. This frequency band is divided into RF carriers of 200 KHz bandwidth, resulting in 125 RF carriers. Each frequency carrier is further divided into 8 logical channels. Therefore, in GSM, each Mobile is allocated one RF carrier and one time slot, which is repetitive within a Frame.
Various encryption algorithms are used to provide secure communication between two mobiles in the GSM system. GMSK (Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying) modulation scheme is used to modulate the information bits before RF frequency conversion.
Key features of GSM
- Standardization: A globally recognized standard for mobile communication.
- Voice and SMS Services: Offers reliable voice calls and SMS messaging.
- Roaming Capability: Seamless connectivity across different regions and countries.
- Spectrum Efficiency: Uses TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) and FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access) for efficient spectrum usage.
- Encryption and Security: Ensures secure communication using encryption algorithms.
- Data Communication: Supports low speed data services like WAP and MMS.
Advantages of GSM
Following are some of the benefits of GSM technology:
- Global Coverage: Provides wide area and international connectivity.
- Cost Effective: Affordable services due to widespread infrastructure.
- Interoperability: Compatible with multiple mobile devices and networks.
- Reliable Communication: Ensures consistent and dependable voice and SMS services.
Conclusion
GSM has laid the foundation for modern mobile communication, offering reliability, scalability, and global accessibility. Its features continue to influence next-generation wireless technologies, ensuring users stay connected wherever they are.
Advertisement
 RF
RF