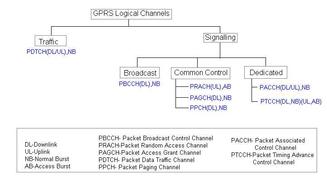
GSM OSS vs BSS: Understanding the Core Network and Base Station Subsystem
Advertisement
The figure depicts GSM Network Architecture.
As shown, the GSM system is composed of the following three main parts:
- Base Station Subsystem (BSS)
- OSS (Operation and Support System) OR NSS (Network Subsystem or Network Switching Subsystem)
- Mobile Subscriber Station (MS)
GSM is used for cellular communication. Like GSM there are other wireless standards such as CDMA, Mobile WiMAX and LTE which are used for cellular voice and data communication. Refer to the Cellular Communication Tutorial.
 image alt: GSM OSS vs BSS
image alt: GSM OSS vs BSS
OSS is also referred to by the name CN (Core Network).
GSM OSS - Operation and Support System
GSM OSS is composed of the following subsystems:
- MSC - Mobile Services Switching Center
- VLR - Visitor Location Register
- HLR - Home Location Register
- AUC - Authentication Center
- EIR - Equipment Identity Register
- OMC - Operation and Maintenance Center
- Data communication network
Following are the functions of GSM OSS:
- Mobility Management
- Call handling
- Subscriber data management such as plans, name, address, billing cycle etc.
- Switching of calls between cellular to cellular, between cellular and PSTN, between CS and PS etc.
- Authentication and equipment validation
- It houses MSC and GMSC which take care of switching related functionalities desired on GSM mobile system.
- In order to perform above functions OSS is divided into databases (or registers) and switches.
HLR is the master database which stores permanent information of subscribers.
VLR is a temporary database of visiting subscribers in the area.
AUC takes care of subscriber authentication.
EIR takes care of handset verification.
GSM BSS - Base Station Subsystem
GSM BSS resides between MS and GSM OSS (or NSS).
GSM BSS is composed of the following subsystems:
- BTS - Base Transceiver Station
- BSC - Base Station Controller
Following are the functions of GSM BSS:
- It performs functions specific to radio access techniques used.
- Its primary function is to communicate with MS in a certain area as covered by Core Network (CN, made of MSC/VLR)
- Radio equipments in BSS cover one or more cells.
- BTS part provides services in a cell.
BTS works as per commands by the BSC.
BTS also performs functions such as channel coding, encryption, decryption on the radio interface as well as transcoding and rate adoption.
BSC controls one or more BTS.
The primary function of BSC is to control the radio resources of GSM RAN (Radio Access Network).
The other functions of BSC include radio resource management, intercell handovers, control of BTS, power control etc.
Advertisement
 RF
RF