SMS Network Architecture and Key Elements
Advertisement
This article covers the following aspects of SMS:
- SMS basics and types
- SMS network and elements
- SMS MO (Mobile Originated) and MT (Mobile Terminated) call flow
- SMS versus MMS
SMS Network Elements
The SMS network in GSM is composed of the following network elements:
- SMSC (Short Message Service Center)
- HLR (Home Location Register)
- MSC (Mobile Switching Center)
- VLR (Visitor Location Register)
- BSC (Base Station Controller)
- BTS (Base Transceiver Station)
- MS (Mobile Station) or UE (User Equipment)
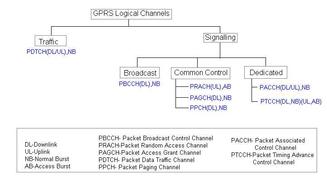
SMS Transmission
SMS messages are carried by the signaling channel (specifically, SDCCH - Standalone Dedicated Control Channel) on the air interface between the MS and the BTS. From there, the SMS is transported using the SS7 signaling protocol through the BSC, MSC/VLR, and finally to the SMSC.
Advertisement
 RF
RF