ATM vs STM: Asynchronous vs Synchronous Transfer Modes Explained
Advertisement
This article compares Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) and Synchronous Transfer Mode (STM), highlighting their differences.
ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode)
ATM utilizes statistical multiplexing to efficiently transmit data.

- Operation:
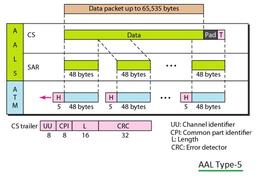
- Upper-layer data is divided into packets of 48 bytes each.
- A header is added to each packet, creating an ATM cell.
- Packets are transmitted only when there’s data to send, making it efficient.
- Statistical Multiplexing: ATM uses statistical multiplexing.
- Advantages: It’s better than STM because no bandwidth is wasted when a source is idle.
- Disadvantages: The added header introduces overhead, causing delays as packets traverse the network.
STM (Synchronous Transfer Mode)
STM operates similarly to Time Division Multiplexing (TDM).

- Operation:
- STM assigns dedicated bandwidth to each source.
- Each source gets a periodic turn for transmission.
- No header is added to packets.
- Advantages: The absence of headers means no overhead and fixed delays.
- Disadvantages: It’s unsuitable for bursty traffic sources. Alloted bandwidth is wasted when a source is idle.
Key Differences: ATM vs. STM
| Feature | ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) | STM (Synchronous Transfer Mode) |
|---|---|---|
| Multiplexing | Statistical | Synchronous (TDM-like) |
| Header | Present | Absent |
| Bandwidth Allocation | On-demand | Dedicated |
| Overhead | High | Low |
| Delay | Variable | Fixed |
| Bursty Traffic | Suitable | Unsuitable |
| Idle Source | No Bandwidth Used | Bandwidth Wasted |
Advertisement
 RF
RF