NB-IoT Interview Questions and Answers
Advertisement
This document presents a list of questions and answers related to NB-IoT (Narrowband Internet of Things). This questionnaire aims to help individuals prepare for job interviews related to NB-IoT skills and can also be a valuable resource for engineering students during vivas.
NB-IoT Questions and Answers
Question 1: What is NB-IoT, and what are its primary use cases?
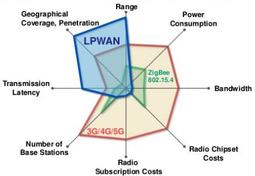
Answer 1: NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT) is a low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) technology standardized by 3GPP. It’s designed for IoT applications that require low data rates, extended battery life, and widespread coverage.
Its primary use cases include:
- Smart metering (e.g., water, gas, electricity)
- Environmental monitoring (e.g., air quality, pollution levels)
- Asset tracking (e.g., containers, vehicles, livestock)
- Smart agriculture (e.g., soil moisture, weather conditions)
- Smart city applications (e.g., smart parking, street lighting)
These applications benefit from devices that can operate for long periods on a single battery, often in challenging radio environments like deep indoors or remote locations.
Question 2: How does NB-IoT differ from other LPWAN technologies like LoRa and Sigfox?
Answer 2: NB-IoT distinguishes itself from LoRa and Sigfox primarily through its use of licensed spectrum. This provides more reliable and secure communication compared to the unlicensed nature of LoRa and Sigfox.
Here’s a breakdown:
- Spectrum: NB-IoT operates in licensed spectrum, while LoRa and Sigfox use unlicensed spectrum.
- Reliability & Security: Licensed spectrum offers more predictable performance and reduces the risk of interference.
- Coverage & Density: NB-IoT generally provides better coverage in urban environments and supports higher device density per cell.
- Integration: NB-IoT is designed for seamless integration with existing cellular networks, leveraging established infrastructure.
- Deployment: LoRa and Sigfox offer greater flexibility in network deployment, as they don’t rely on cellular operators.
In essence, NB-IoT is well-suited for large-scale, carrier-grade IoT deployments where reliability and security are paramount, while LoRa and Sigfox cater to more flexible and localized deployments.
Question 3: What are the key features of NB-IoT that make it suitable for IoT applications?
Answer 3: Several key features make NB-IoT a compelling choice for IoT applications:
- Low Power Consumption: Devices can operate for up to 10 years on a single battery, minimizing maintenance and replacement costs.
- Wide Area Coverage: NB-IoT supports deep indoor and rural area coverage with a link budget of 164 dB, ensuring connectivity even in challenging environments.
- Low Data Rates: Optimized for applications that transmit small amounts of data infrequently, reducing network congestion and power consumption.
- High Connection Density: Supports a large number of devices per cell, up to 100,000, making it suitable for dense deployments like smart cities.
- Licensed Spectrum: Provides secure and reliable communication with minimal interference, ensuring data integrity.
Question 4: Explain the concept of Power Saving Mode (PSM) in NB-IoT.
Answer 4: Power Saving Mode (PSM) is a crucial feature in NB-IoT designed to minimize energy consumption. When a device enters PSM, it essentially goes into a deep sleep state for extended periods.
During PSM:
- The device remains registered with the network.
- It does not transmit or receive data.
- Power consumption is reduced to an absolute minimum.
The device wakes up periodically (based on configured timers) or when triggered by the application to send data. This is ideal for applications that require infrequent communication, such as remote sensor monitoring.
Question 5: What is the difference between NB-IoT and LTE-M?
Answer 5: NB-IoT and LTE-M (LTE Cat-M1) are both 3GPP-standardized LPWAN technologies, but they cater to different IoT use cases.
Here’s a comparison:
| Feature | NB-IoT | LTE-M (LTE Cat-M1) |
|---|---|---|
| Power Consumption | Ultra-low | Low |
| Data Rates | Very low (up to 250 kbps) | Higher (up to 1 Mbps) |
| Mobility | No support | Supports mobility (handover between cells) |
| Voice Support | No support | Supports voice (VoLTE) |
| Coverage | Deep indoor coverage | Good coverage |
| Use Cases | Static sensors, meters, asset tracking | Wearables, vehicle tracking, real-time monitoring |
In summary, NB-IoT is optimized for ultra-low power and deep coverage, while LTE-M supports higher data rates, mobility, and voice, making it suitable for applications requiring more bandwidth and real-time communication.
Question 6: How does NB-IoT achieve extended coverage in challenging environments?
Answer 6: NB-IoT employs several techniques to achieve extended coverage, particularly in challenging environments:
- Narrowband Operation: The use of a narrow bandwidth (200 kHz) allows for better signal penetration and improved resilience against interference. Think of it like focusing a beam of light – the narrower the beam, the farther it reaches.
- Repetition: Data is transmitted multiple times. This increases the probability of successful reception, especially in areas with weak signal strength.
- Higher Power Spectral Density: By concentrating power within a narrower bandwidth, the NB-IoT signal can travel farther and penetrate deeper into buildings. This essentially amplifies the signal strength within the limited bandwidth.
Question 7: What are the typical data rates supported by NB-IoT, and why are they sufficient for IoT applications?
Answer 7: NB-IoT supports data rates of up to 250 kbps. While this may seem low compared to broadband technologies, it’s sufficient for many IoT applications.
The rationale is that many IoT devices transmit small amounts of data intermittently, such as:
- Sensor readings (e.g., temperature, pressure)
- Status updates (e.g., device online/offline)
- Control commands (e.g., turn on/off a light)
These applications don’t require high-speed data transfer. The lower data rates of NB-IoT are a deliberate design choice to prioritize extended battery life and reduce network congestion.
Question 8: What are the benefits of using NB-IoT in smart city applications?
Answer 8: NB-IoT offers significant benefits for smart city deployments:
- Long Battery Life: Reduces the need for frequent maintenance and battery replacement, minimizing operational costs.
- Deep Coverage: Ensures reliable connectivity in challenging locations such as underground parking garages, basements, or remote areas.
- Scalability: Supports a large number of connected devices, enabling widespread deployment of smart sensors and meters throughout the city.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Operates on existing cellular infrastructure, minimizing the cost of deployment and management compared to building dedicated networks.
Examples include smart parking systems, smart street lighting, waste management monitoring, and environmental sensing.
Question 9: How does NB-IoT ensure secure communication for IoT devices?
Answer 9: NB-IoT incorporates several security measures to protect IoT device communication:
- Use of Licensed Spectrum: Reduces the risk of interference and unauthorized access compared to unlicensed spectrum options.
- Built-in Encryption: Employs standardized cellular encryption protocols, such as 128-bit AES, to protect data integrity and confidentiality during transmission.
- Authentication and Authorization: Relies on SIM-based authentication, ensuring that only authorized devices can access the network. This provides a strong layer of security, as each device is uniquely identified and authenticated.
Question 10: What challenges might be faced when deploying NB-IoT, and how can they be addressed?
Answer 10: While NB-IoT offers numerous advantages, some challenges can arise during deployment:
-
Coverage Limitations in Very Remote Areas: Although NB-IoT provides excellent coverage, extremely remote or sparsely populated regions may still experience connectivity issues.
- Solution: Consider using satellite-based IoT solutions or deploying additional NB-IoT infrastructure in those areas.
-
Integration with Legacy Systems: Integrating NB-IoT devices with existing systems might require custom interfaces or software development.
- Solution: Utilize middleware solutions or APIs to facilitate seamless integration between NB-IoT devices and legacy systems.
-
Limited Bandwidth: While sufficient for many IoT applications, the narrow bandwidth may not be suitable for applications requiring higher data rates.
- Solution: For applications demanding higher bandwidth, consider a complementary use of other technologies like LTE-M or 5G alongside NB-IoT, depending on the specific requirements.
Advertisement
 RF
RF