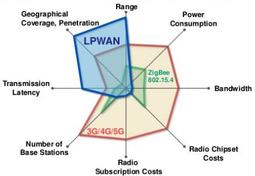
Mioty vs. Traditional LPWAN: A Detailed Comparison
Advertisement
As IoT networks become increasingly sophisticated, the choice of communication technology is paramount for ensuring reliability, efficiency, and scalability. Mioty and traditional LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network) technologies like LoRa, Sigfox, and NB-IoT have all emerged as popular solutions for low-power, long-range communication. While they cater to similar applications, Mioty distinguishes itself with its Telegram Splitting Multiple Access (TSMA) protocol, offering unique advantages in interference resistance and scalability.
In this article, we’ll explore the key differences between Mioty and traditional LPWAN technologies, highlighting their features, advantages, and best-use cases.
Mioty vs. Traditional LPWAN: Key Differences
The following table provides a side-by-side comparison of Mioty and traditional LPWAN technologies:
| Feature | Mioty | Traditional LPWAN Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Based on ETSI TS 103 357, using telegram splitting for robust communication. | Uses direct message transmission without splitting, making it prone to interference. |
| Scalability | Can handle up to 1.5 million messages per day per base station. | Typically supports fewer messages due to network congestion in high-density areas. |
| Interference Resilience | High interference tolerance due to splitting messages into smaller sub-packets sent across different frequencies and times. | More susceptible to interference and packet loss in noisy RF environments. |
| Energy Efficiency | Extremely low power consumption, enabling devices to operate for years on a single battery. | Also energy efficient but may vary depending on protocol and network traffic. |
| Range | Supports up to 15 km in rural areas and several kilometers in urban settings. | Comparable range, but performance can degrade more in interference-heavy environments. |
| Bandwidth Efficiency | Transmits small sub-packets over ultra-narrow bandwidth, optimizing spectrum use. | Typically uses narrowband, but not as efficient in crowded spectrum environments. |
| Message Integrity | High reliability due to redundancy and robust error correction in telegram splitting. | May experience more packet loss or require retransmissions in noisy conditions. |
| Deployment Complexity | Slightly more complex due to telegram splitting technology and system design. | Easier deployment with well-established infrastructure and ecosystem support. |
| Standardization | Fully standardized under ETSI TS 103 357. | Standards vary (e.g., LoRaWAN is standardized by LoRa Alliance, while Sigfox is proprietary). |
| Ecosystem Maturity | Emerging technology with growing adoption and ecosystem. | Established ecosystem with widespread adoption and support. |
| Use Cases | Ideal for industrial IoT, smart utilities, and large-scale deployments requiring high scalability and reliability. | Suitable for smaller-scale deployments or applications with lower reliability demands. |
Conclusion
Understanding the nuances between Mioty and traditional LPWAN technologies is crucial for selecting the optimal solution for your IoT deployment. While traditional LPWANs offer proven reliability, Mioty introduces significant improvements in scalability, energy efficiency, and interference handling. Carefully evaluating these distinctions will help you choose the technology that best meets the specific requirements of your IoT network.
 RF
RF