AWG (Arbitrary Waveform Generator) Basics
Advertisement
This article delves into the fundamentals of AWGs (Arbitrary Waveform Generators), exploring their different types (traditional and DDS-based) and comparing them to conventional waveform generators. As we know, an AWG generates vector signal waveforms based on a user-defined waveform file, which can be written or loaded into its memory.
Nowadays, AWG modules are frequently integrated into Vector Signal Generators (VSGs). These modules are utilized in a wide range of applications compliant with IEEE or 3GPP standards like WLAN, WiMAX, radar, GSM, LTE, and more.
Within an RF VSG, the AWG is responsible for generating baseband waveforms according to these standards. The generated RF vector can then be used to test the receiver components of complex devices adhering to the same standards.

AWG Arbitrary Waveform Generator basics
As depicted in Figure 1, a standard AWG clocks user-stored waveform samples from memory and transfers them to a DAC (Digital-to-Analog Converter). These resulting analog waveforms are then filtered to produce the desired output waveform.
The waveform’s signal and shape are determined by several factors:
- Sampling rate
- Size of memory (number of time samples)
- Vertical resolution
- DAC characteristics
- Signal conditioning blocks (amplitude control using attenuators and amplifiers)
- Filters, and more.
Comparison Between AWG and Conventional Waveform Generators
The following table summarizes the key differences between AWGs and older, simpler waveform generators.
| Conventional Function Generator | Arbitrary Function Generator (AFG or AWG) |
|---|---|
| Standard waveforms only | Any wave shape can be obtained |
| Design is predominantly analog | Design is digital |
| Wave shape cannot be stored | Wave shape can be stored |
| Specifications are analog-based | Specifications are digital-based |
| Wave shape adjustment under computer control is generally not possible | Wave shape adjustment under computer control is possible with a variety of techniques |
Traditional AWG vs. DDS-Based AWG Types
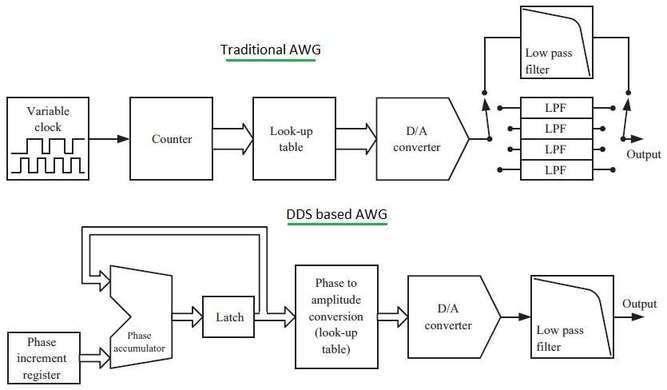
traditional AWG vs DDS based AWG
Arbitrary waveform generators are used to create baseband waveform signals. They all use the same clocks, DACs, memories, and filters, etc. There are two primary types of AWGs:
- Traditional AWG
- DDS (Direct Digital Synthesis) based AWG
A traditional AWG employs a variable sample clock and segments of a look-up table. This look-up table contains information representing the amplitude of the output signal. Each location within the table corresponds to a single point in the waveform to be generated.
A DDS-based AWG, on the other hand, utilizes a fixed clock, a phase increment register, a phase accumulator, and a latch. Traditional AWGs typically require multiple LPFs (low pass filters), whereas DDS-based AWGs usually only need one.
Advertisement
 RF
RF
