
WLAN 802.11ac Frame Format Explained
Explore the 802.11ac frame format, its components (L-STF, L-LTF, L-SIG, VHT-SIG-A/B, VHT-STF, VHT-LTF, Data), and their functions for 11ac compliant frames.
Advertisement

Explore the 802.11ac frame format, its components (L-STF, L-LTF, L-SIG, VHT-SIG-A/B, VHT-STF, VHT-LTF, Data), and their functions for 11ac compliant frames.

Explore the 802.11ac MAC layer: frame format, aggregation (A-MPDU), management frames, and key features for efficient WLAN networks.

Explore the 802.11ad physical layer, covering Control, Single Carrier, OFDM, and Low Power SC PHY configurations. Learn about packet structure, preamble, header, and payload.

Learn about WiFi 6 (802.11ax) basics, features, frame structure, physical and MAC layers. Improve efficiency, speed, and capacity in wireless networks.

Learn the fundamentals of Wireless Local Loop (WLL) for broadband internet, its benefits, frequency bands, and challenges. Understand how WLL provides fixed wireless connections.

Explore the X.25 protocol stack, including the physical (X.21), frame (LAPB), and packet (PLP) layers. Learn about frame structure and how these layers ensure robust network communication.

Explore the Z-Wave physical layer (PHY) functions, data rates, modulation, and coding schemes. Learn about RF profiles, frame transmission, and link quality.
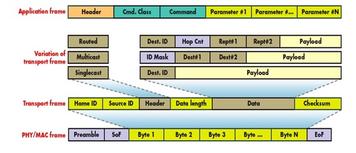
Explore the Z-Wave protocol stack, including the PHY, MAC, Transport, Network, and Application layers. Learn about frame routing, network topology, and application command classes.

Explore Z-Wave RF PHY conformance tests for device testing, covering transmitter (frequency error, RF data rate, power) and receiver (sensitivity, blocking, turnaround time) measurements.

Explore the basics of Z-Wave security, including message freshness, encryption, data authentication, and the key exchange protocol used in Z-Wave networks.

Explore Z-Wave technology: features, frequency bands, network architecture, frame structure, protocol stack, and security aspects. Ideal for IoT and home automation applications.

Learn about Zigbee 3.0, its key features, protocol stack, security, and benefits for creating interoperable and robust IoT networks.

An overview of the Zigbee AODV routing protocol, including address discovery, route discovery, broadcast transmissions, unicast transmissions, and the AODV algorithm.
Explore Zigbee frequency bands (868 MHz, 915 MHz, and 2450 MHz) and their respective data rates, modulation types, and channel allocations within the ISM bands.

Learn the fundamentals of Zigbee mesh networks, including topologies, features, advantages, and disadvantages. Explore its role in low-power wireless applications.

Understand the Zigbee physical layer (PHY), including 868/915MHz and 2450MHz formats, modulation techniques, and the PPDU frame structure.
Explore the Zigbee physical layer frame format, focusing on the components of the PPDU, including the preamble, SFD, frame length, and PSDU.

Explore the Zigbee protocol stack's seven layers, from Physical to Application, designed for reliable, low-power IoT communication. Understand each layer's function and architecture.

An overview of Zigbee network architecture, covering basics, frame structure, protocol stack layers, and application layer profiles.
Advertisement