Ka Band: Frequencies, Advantages, and Applications
Advertisement
This page details Ka Band frequency values, applications, and advantages.
| Frequency Band Designation | Frequency Range | Wavelength |
|---|---|---|
| Ka Band | 27 to 40 GHz | 1.1 to 0.75 cm |
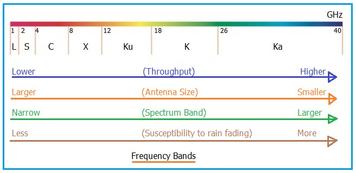
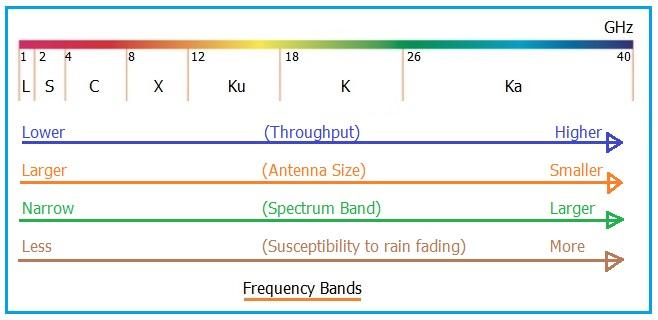
The Ka band frequencies reside above the K Band in the frequency spectrum, as illustrated in Figure 1 below. As the table indicates, the Ka band spans from 27 GHz to 40 GHz, corresponding to wavelengths of 0.75 to 1.1 centimeters.
Ka Band Frequency Advantages
Compared to other frequency bands, Ka Band offers several benefits:
- High-Speed Data Communication: Enables rapid data transfer.
- Smaller Dish Antennas: Allows for the use of smaller dish antennas, typically with diameters around 0.9 meters.
- Cheaper and Easier Installation: The reduced antenna size leads to simplified and more cost-effective installations.
However, Ka band also has some drawbacks:
- Significant Signal Attenuation: Susceptible to rain fade, which can weaken signals.
- Greater Rain Dissipation: Rain absorbs more energy at Ka band frequencies compared to Ku band.
- Limited Availability: Not accessible for communication in all locations worldwide.
Ka Band Frequency Applications
The applications of Ka Band Frequency are diverse:
- Communication Satellites: Used for satellite communication links.
- Close-Range Radars: Suitable for high-resolution, short-distance radar systems.
- Space Telescopes: Facilitates the transmission of data collected by space telescopes back to Earth for scientific analysis via Ka band downlink frequencies.
- Satellite Networks: Employed in Inmarsat and will be featured in the Iridium Next series of satellites.
Advertisement
 RF
RF