VSI vs. CSI: Voltage Source Inverter vs. Current Source Inverter
Advertisement
Voltage source inverters (VSI) and current source inverters (CSI) are two types of inverters used in power electronics to convert DC (direct current) to AC (alternating current). They have distinct characteristics and applications, making them suitable for different use cases. Let’s dive into the details of each type.
Voltage Source Inverter (VSI)
-
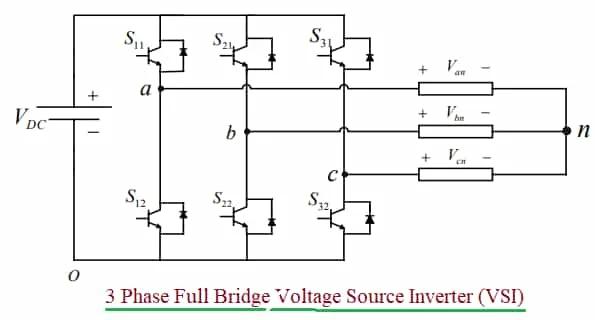
Input Configuration: The input to a VSI is typically a constant or regulated DC voltage source. This makes them ideal for applications where a stable voltage supply is available, such as renewable energy systems, motor drives, and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS).
-
Control Method: In a VSI, the output voltage is controlled by adjusting the duty cycle of the switching devices (usually insulated gate bipolar transistors - IGBTs) in the inverter circuit. The output voltage is adjusted to meet the desired frequency and amplitude required by the AC load. Think of it like finely tuning the voltage output to match what your device needs.
-
Output Characteristics: VSIs generally provide a low-impedance output. They are designed to act as stiff voltage sources, meaning they can maintain a relatively constant output voltage even under varying load conditions. They are very stable even if load fluctuates.
-
Applications: VSIs are widely used in variable speed motor drives, grid-tied photovoltaic inverters, UPS systems, and various other applications requiring controlled AC output.
Current Source Inverter (CSI)
-
Input Configuration: The input to a CSI is typically a constant or regulated DC current source. CSIs are less common than VSIs and are used in applications where maintaining a constant current is essential, such as in certain types of motor drives and induction heating systems.
-
Control Method: In a CSI, the output current is controlled by adjusting the switching frequency and pulse width of the inverter circuit. The inverter ensures that the output current remains constant, adjusting the voltage as needed to achieve this constant current.
-
Output Characteristics: CSIs provide a high-impedance output. They act as stiff current sources, meaning they can maintain a relatively constant output current even when the load conditions change.
-
Applications: CSIs are found in applications where maintaining a constant current is crucial, such as high-power drives, induction heating, and certain types of motor drives with specific control requirements.

VSI vs. CSI: A Detailed Comparison
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences between Voltage Source Inverters and Current Source Inverters:
| Feature | Voltage Source Inverter | Current Source Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Input configuration | DC voltage source | DC current source |
| Output characteristics | Low impedance output | High impedance output |
| Control Method | Output voltage controlled by adjusting the duty cycle of switching devices | Output current controlled by adjusting switching frequency and pulse width |
| Performance in overload conditions | Generally robust and performs well under varying load conditions | May have better performance in overload conditions |
| Output Adjustment | Adjusts output voltage to meet load requirements | Adjusts output current to meet load requirements |
| Construction | Complex, requires feedback diodes | Simple, absence of feedback diodes |
| Variation in output voltage | Varies slightly due to capacitor | Varies due to change in load |
| Short Circuit (SC) protection | Not possible | Possible |
| Examples | Half bridge, Full bridge, Square wave, PWM inverters | Capacitor commutated current source inverter (CSI) and ASCI (Auto Sequential Commutated Inverter) |
| Common Use Cases | More common and widely used in various applications | Less common, used in specific high-power and specialized applications |
| Applications | Motor drives, Renewable energy systems (e.g., photovoltaic inverters), UPS systems | High power drives, Induction heating systems, Certain motor drives with specific control requirements |
Conclusion
In summary, the key difference lies in the input configuration and the controlled parameter. A Voltage Source Inverter maintains a constant voltage at the output and is more common, while a Current Source Inverter maintains a constant current at the output and is used in specific applications where this characteristic is advantageous. The choice between VSI and CSI depends on the requirements and characteristics of the target application.
Advertisement
 RF
RF



