Linear vs. Rotary Potentiometer: Key Differences
Advertisement
This article compares linear and rotary potentiometers, highlighting their differences and providing insights into their applications.
Introduction:
A potentiometer is a three-terminal device that acts as an adjustable voltage divider through a rotating or sliding contact. When only two terminals (one end and the wiper) are used, it functions as a variable resistor, also known as a rheostat. Potentiometers are widely used for volume and tone controls in audio systems and as position sensors (or transducers) in joysticks, among other applications.
Linear Potentiometer

Figure 1: Linear Potentiometer
- A linear potentiometer, as shown in Figure 1, features an electrical resistance in the form of a straight track.
- This track can be a strip of resistive polymer or an insulator with a coil of nichrome wire wrapped around it.
- For sensing applications, the potentiometer is wired as a voltage divider, with a fixed potential applied across its entire length.
- The wiper slides along the track, resulting in a sensing voltage that varies linearly with the wiper’s position. This characteristic gives it the name “linear potentiometer.”
- The output can directly control an analog indicator in an analog meter or be processed by an Analog to Digital Converter (ADC) for further use.
- Example: Linear potentiometers from companies like Bourns.
Advantages:
- Simple design
- Inexpensive
- Compact size
- Requires few components
Disadvantages:
- Wear occurs due to the wiper’s motion, even with lubricant on the track.
- Vibration or contamination (dirt/moisture) can reduce its lifespan.
Rotary Potentiometer

Figure 2: Rotary Potentiometer
- Rotary potentiometers are divided into arc-segment and multi-turn types.
- Figure 2 illustrates an arc-segment rotary potentiometer, the more common type compared to the multi-turn variant.
- It consists of a resistor in the shape of an arc, known as the track. Like the linear potentiometer, this track can be a strip of resistive polymer or an insulator with a nichrome wire coil.
- The wiper slides along the track, sensing a voltage that varies linearly with the angular position of the wiper.
- The advantages and disadvantages of rotary potentiometers are similar to those of linear potentiometers.
Rotary Encoder
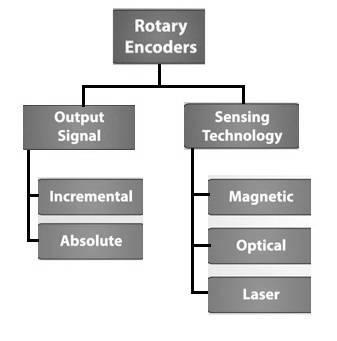
Figure 3: Rotary encoder basics and types
- A rotary encoder is a position sensor used to determine the angular position of a rotating shaft.
- It generates an electrical signal, either analog or digital, which is then sensed or used by a microcontroller board or Arduino to perform the desired action.
Advertisement
 RF
RF



