Analog vs. Digital Filters: Key Differences and Comparison
Advertisement
This page compares analog filters and digital filters, highlighting the differences between them. Both types of filters serve the common purpose of filtering out unwanted frequencies from a signal’s spectrum and allowing desired frequencies to pass through.
Depending on the specific filtering action, filters are categorized as low-pass, high-pass, band-pass, or band-stop filters.
Analog Filter
Analog filters are employed to filter signals before they are converted into digital form. This means they are typically used before an Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) in the circuit, residing primarily in the analog portion of a system.
These filters are constructed using discrete electronic components such as resistors (R), inductors (L), and capacitors (C). RF/Microwave analog filters are often designed using microstrip lines, stripline circuits, or waveguides.
Example: RF Filter based on Microstrip line
Digital Filter
Digital filters, on the other hand, are used to filter signals after the analog signal has been converted to digital form. Therefore, they are placed after the ADC in a circuit, primarily within the digital processing section of the system.
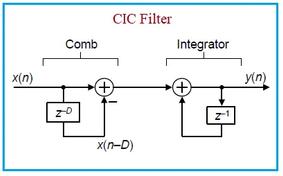
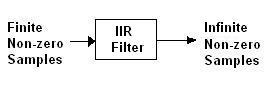
They are generally implemented as Finite Impulse Response (FIR) or Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) filters, typically designed as software and deployed on Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) or Digital Signal Processors (DSPs).
Examples: FIR and IIR filters developed using C or assembly code, or other programming languages. These are then implemented on FPGA/DSP processors.
Analog Filter vs. Digital Filter: A Comparison Table
The following table compares analog filters and digital filters based on their respective advantages and disadvantages:
| Specifications | Analog Filter | Digital Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Programmable coefficients | No | Yes |
| Complexity | Higher, usually seen in high-performance based analog filters. | Lower |
| Latency | Lower | Higher |
| Cost | Higher, depends on the analog components used in the design. | Lower |
| Drift Error, Multichannel Matching Error, Aging | YES | NO |
| Protection feature for ADC input | Available | Not available |
| Additive noise introduction | It adds component-based thermal noise in the bands. | It adds digital noise due to the quantization process. |
Advertisement
 RF
RF