RRH vs. DAS: Understanding the Key Differences
Advertisement
This page compares RRH (Remote Radio Head) and DAS (Distributed Antenna System), highlighting their key differences.
Introduction:
Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS) and Remote Radio Heads (RRH) are both used in wireless communication systems. RRH is a component used in cellular networks to centralize baseband processing and offload RF processing to units located closer to the antennas. DAS, on the other hand, is a system used to distribute wireless signals over a specific area to enhance coverage and capacity, particularly indoors.
Distributed Antenna System (DAS)
A Distributed Antenna System is a network of multiple antennas distributed throughout a specific area to provide enhanced wireless coverage and capacity. The primary goal is to improve signal quality and user experience in environments with high user density and challenging coverage conditions, both indoors and outdoors.

The system typically consists of three main components:
- Central Hub or Headend: This receives wireless signals from the cellular network’s core infrastructure, such as a baseband unit or base station.
- Remote Units (RUs) or Remote Radio Heads (RRHs): These units are located at different points within the coverage area.
- RF Antennas: These antennas are connected to the remote units.
How a DAS Works:
- The central hub receives wireless signals.
- The central hub distributes the signals to the remote units.
- The remote units, equipped with antennas, amplify and retransmit the signals, covering specific zones with strong wireless coverage.
There are three types of DAS antenna systems: passive, active, and hybrid, based on the components used in their design.
RRH (Remote Radio Head)
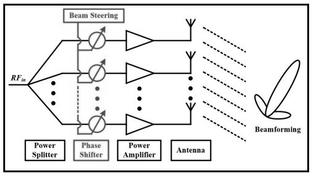
RRH modules are developed according to CPRI and eCPRI standards. They are strategically placed to provide precise coverage and higher data rates, especially in urban areas and high-density regions. Remote Radio Units (RRHs) play a vital role in Mobile WiMAX, 4G LTE, and 5G NR systems.

The figure depicts a base station using RRHs near the antennas. As shown, three RF antennas are interfaced with three Radio Units (REs). These radio units are connected to a single BBU using three fiber optic cables.
An RRH design and installation involves two key elements:
- REC (Radio Equipment Control): Contains the baseband processing blocks.
- RE (Radio Equipment): Contains radio transceivers, amplifiers (PA/LNA), and other components responsible for transmitting and receiving RF signals to and from antennas.
Both REC and RE units are connected using high-speed fiber optic cables.
Difference between RRH and DAS
While both technologies contribute to improved wireless connectivity, they serve different purposes and have distinct architectures.
| Parameters | RRH | DAS |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Separates RF processing and digital baseband processing into two units: RE (RF Front end) and REC (Baseband Unit). | Distributes wireless signals over a specific area. |
| Deployment Architecture | Centralized baseband unit connected to multiple Radio Heads closer to Antennas. | Centralized hub connected to distributed antennas to cover a higher capacity of users. |
| Transport Medium | Fiber optic cables | Coaxial cables |
| Signal Loss | Low signal loss due to shorter cable length between BBU (REC) and Radio Head (RE). | High signal loss due to long coaxial cables. |
| Scalability | Adding more RRHs may require additional fiber connections. | Scalable with added active or passive DAS units or components. |
| Flexibility & Future Upgrades | Allows easy upgrades and modifications to the baseband unit without changing antennas. Easy to upgrade baseband software for new cellular standard releases or version changes. | Provides flexibility in addressing specific coverage challenges; baseband software upgrades are not possible. |
| Application | Outdoor cell sites, small cell deployments, 5G mmWave, and dense networks. | Indoor environments, large buildings, stadiums, concerts, etc. |
RRHs are often an integral part of Distributed Antenna Systems. They are frequently used to provide indoor wireless coverage in large buildings, airports, stadiums, and other venues. RRHs help distribute radio frequency (RF) signals to multiple remote antenna units to ensure uniform coverage.
 RF
RF