Mechanical vs. Electrical Systems: An Analogy
Advertisement
This article explores the analogy between mechanical and electrical systems, highlighting their similarities and differences.
Introduction:
Two systems, mechanical and electrical, are considered analogous when their differential equations are the same. Though they achieve this behavior through different physical components, the underlying mathematical relationships are equivalent.
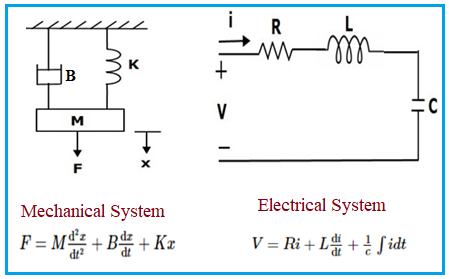
Mechanical System
-
The figure above illustrates a mechanical system comprised of a mass (‘m’) attached to a spring. ‘B’ represents damping, ‘K’ is the spring constant, and ‘X’ denotes the displacement caused by the applied Force (‘F’).
-
The second-order differential equation describing this system can be written as:
F = M(d²x/dt²) + B(dx/dt) + K*x …Equation-(1)**
Electrical System
-
The figure also shows a Series LCR electrical system.
-
This system consists of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), all connected in series.
-
When an input voltage (V) is applied across the terminals, a current (i) flows through the circuit.
-
Applying Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) to the loop, we arrive at the following equation:
- V = Ri + Ldi/dt + (1/C)∫idt
-
Substituting (dq/dt) in place of “i” in the above equation, we obtain the differential equation for the electrical system as:
- V = R*dq/dt + L * d²q/dt² + q/C
-
Rearranging, we get:
V = L * d²q/dt² + R*dq/dt + q/C …Equation-(2)
Difference Between Mechanical and Electrical Systems
The following table highlights the differences between mechanical and electrical systems by comparing their analogous parameters:
| Mechanical system | Electrical system |
|---|---|
| Force (F) | Voltage (V) |
| Mass (M) | Inductance (L) |
| Frictional Coefficient (B) | Resistance (R) |
| Spring Constant (K) | Reciprocal of Capacitance (1/C) |
| Displacement (x) | Charge (q) |
| Velocity (v) | Current (i) |
 RF
RF


