AMQP Protocol: Advantages and Disadvantages
Advertisement
This page explores the advantages and disadvantages of the AMQP (Advanced Message Queuing Protocol) protocol, commonly used in IoT (Internet of Things) applications.
What is AMQP?
Introduction: AMQP stands for Advanced Message Queuing Protocol. It operates over the TCP layer and utilizes a publish/subscribe architecture, similar to MQTT. AMQP facilitates asynchronous message transfer, making it OS, hardware, and programming language agnostic. It employs optimized data framing with a buffering approach, significantly enhancing server performance. Security is provided through TLS and SASL.
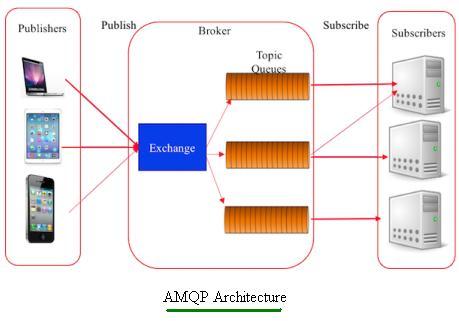
The figure above illustrates the AMQP architecture.
As shown, an AMQP broker includes exchanges and queues. Publishers send messages with specific routing keys to the exchange. The exchange then uses these keys to route messages to the appropriate queues. Messages remain stored in the queues until they are delivered to, or read by, subscribers. Bindings define the rules for connecting exchanges to queues. There are three exchange types: direct exchange, fanout exchange, and topic exchange.
Benefits or Advantages of AMQP
Here are the key benefits of using AMQP:
- Guaranteed Quality of Service (QoS): AMQP uses QoS, ensuring the reliable delivery of important data.
- Established Publish/Subscribe Architecture: AMQP leverages the proven publish/subscribe model, similar to MQTT, for efficient data sharing.
- Interoperability: It guarantees interoperability because it is a wire-level protocol that transmits data as a stream of bytes.
- Simplified Peer-to-Peer Communication: AMQP facilitates straightforward peer-to-peer communication, even with intermediaries.
- Evolvability: The protocol is designed to adapt and work with evolving standards.
- Secure Connections: AMQP offers secure connections to users through protocols like SSL, similar to CoAP, MQTT, HTTP, and XMPP.
Drawbacks or Disadvantages of AMQP
Despite its strengths, AMQP has some drawbacks:
- Lack of Backward Compatibility: AMQP is not backward compatible with older versions, which may create issues when integrating with legacy systems.
- Complexity: It is more complex than simpler wire protocols like HTTP 1.0 or HTTP 1.1.
- Higher Bandwidth Requirements: AMQP typically requires more bandwidth compared to lightweight protocols like MQTT, CoAP, or XMPP.
- Limited Resource Discovery: Unlike CoAP, HTTP, and XMPP, AMQP lacks built-in support for resource discovery.
Advertisement
 RF
RF



