GSM Synchronization Channel (SCH) Explained
Advertisement
This page describes the GSM Synchronization Channel (SCH). After a mobile device achieves frequency synchronization with a Base Transceiver Station (BTS), it needs to synchronize in time. This time synchronization is accomplished using the GSM SCH, which the BTS transmits in the downlink.
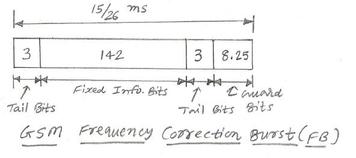
SCH stands for Synchronization Channel. It uses the Synchronization Burst (SB). The SCH carries the frame number and the BSIC (Base Station Identity Code). This information helps the mobile device synchronize with the GSM frame structure and identify the base station within the GSM network.
The SCH is carried within a 51-frame multiframe structure and follows the FCCH (Frequency Correction Channel) in the GSM TDMA frame. The SCH carries 25 bits of information, divided into 19 bits representing the reduced frame number and 6 bits for the BSIC.
The 6 bits of the BSIC are further divided into:
- 3 bits of BCC (Base Station Color Code)
- 3 bits of NCC (Network Color Code)
Here’s a visual representation of SCH processing:

- 25 bits of SCH information are appended with 10 bits of CRC, resulting in 35 bits.
- 4 tail bits of all zeros are added to the 35 bits, yielding a total of 39 bits of uncoded data.
- These 39 bits of data are fed into a rate 1/2 convolutional encoder, which produces 78 bits of coded data.
- This coded data fits neatly into the information field of the Synchronization Burst (SB), and no interleaving is performed on this data set.
- This SB is then modulated and transmitted over the air from the BTS to the GSM Mobile or UE (User Equipment).
Advertisement
 RF
RF